Strongest 3D Printer Filament: 4 Safe Materials You Can Trust
¡Bienvenido a mi blog!
¡Me encanta tenerte aquí! Antes de profundizar en el contenido, me encantaría que me acompañaras en mis redes sociales. Es donde comparto información adicional, conecto con nuestra increíble comunidad y te mantengo al tanto de las últimas noticias. Así es como puedes mantenerte conectado:
📘 Facebook: Shanghai Leierwo Industria Comercio Co., Ltd.
¡Ahora, emprendamos este viaje juntos! Espero que el contenido aquí te resulte no solo revelador, sino también inspirador y valioso. ¡Comencemos!
Tabla de contenido
Key Takeaways (What You’ll Learn)
- Understand what makes a filament the strongest 3D printer filament
- Learn 4 safe and powerful filament materials
- Compare strength, temperature resistance, and printing difficulty
- Know how to choose the best filament for your project
- Get real-world performance data and expert insights
- Read FAQ with AI-style user questions
- Use a comparison table for fast decision-making
Introducción
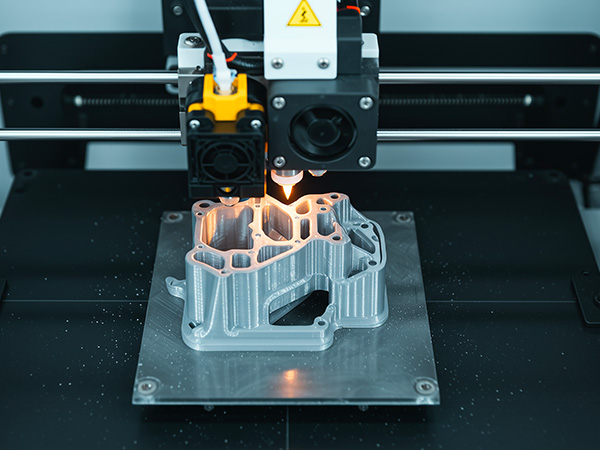

If you’re building functional parts like brackets, gears, or structural prototypes, strength is non-negotiable. Many hobbyists focus only on “printability,” but real-world use demands materials that can handle high stress, heat, and impact.
So when people ask for the strongest 3d printer filament, they are really asking for the most reliable material that can survive real conditions.
In this guide, we’ll explore 4 of the strongest 3D printer filament materials, how they perform in practice, and which one suits your project best.
Understanding What Makes a Filament the Strongest
Tensile Strength vs Impact Strength
A filament can be strong in two different ways: tensile strength and impact strength. Tensile strength measures how much pulling force it can withstand, while impact strength measures how well it resists sudden shocks.
A filament that scores high in both is often considered the strongest 3d printer filament.
Why Temperature Resistance Matters
In real applications, parts may heat up inside machines, in outdoor environments, or near motors or electronics. If the material softens under heat, strength becomes meaningless.
Layer Adhesion Determines Real Strength
Even if the filament itself is strong, poor layer bonding can make the printed part weak. So the strongest 3d printer filament must also have excellent layer adhesion.
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Nylon – The True Strength King
What Makes It Strong
Carbon fiber nylon is nylon mixed with short carbon fibers, creating a composite that combines nylon’s toughness with carbon fiber’s stiffness. The carbon fibers act like tiny reinforcement bars inside the plastic, preventing deformation under load and improving the material’s resistance to bending and stretching.
In practical terms, carbon fiber nylon offers a strength-to-weight ratio far higher than most filaments. This is why it is often the top choice for engineering-grade applications where both strength and durability are required.
Key Properties
- Tensile Strength: 50–70 MPa
- Heat resistance: 120–140°C
- Excellent stiffness and dimensional stability
- Strong layer adhesion when printed at correct temperatures
- Low creep compared to standard nylon
Additionally, carbon fiber nylon has improved wear resistance. This makes it suitable for parts that rub against other components, such as bearings, sliders, and gear housings.
Mejores casos de uso
This material is ideal for structural components, high-stress mechanical parts, and functional prototypes that must withstand real-world loads. It is especially effective for parts such as:
- Robotic arms and joints
- Drone frames
- Tooling fixtures and jigs
- Automotive brackets
- Load-bearing housings
Real-World Example
In an industrial test, carbon fiber nylon gears lasted 3–5 times longer than standard PLA gears under continuous load. Another case from a robotics company showed that switching from regular nylon to carbon fiber nylon reduced failure rate by nearly 30% in high-stress actuators.
Print Challenges
Carbon fiber nylon requires a hardened steel nozzle because carbon fibers are abrasive and will quickly wear down brass nozzles. It also requires high printing temperatures (260–280°C) and a heated bed to prevent warping. Because of its rigidity, it is not suitable for flexible or elastic parts.
Polycarbonate (PC) – High Heat + High Strength
Why Polycarbonate is Strong
Polycarbonate is a widely recognized engineering plastic with excellent strength and temperature resistance. It is known for its ability to withstand heavy loads and sudden impacts without cracking. This is why PC is used in demanding industries such as automotive and aerospace.
PC’s molecular structure provides strong interlayer bonding when printed properly, resulting in parts that can handle real mechanical stress.
Key Properties
- Tensile Strength: 60–70 MPa
- Heat resistance: 150–160°C
- High impact resistance
- Excellent dimensional stability
- Good transparency (for certain variants)
What Makes It a Top Contender
PC is often used in automotive parts, protective gear, and durable housings because of its high durability and heat resistance. It can maintain mechanical properties at temperatures where PLA and PETG would soften.
Real Data
According to material databases, PC has higher impact resistance than PLA and ABS. For example, PC’s Izod impact strength is typically 5–10 times higher than PLA’s, making it one of the most impact-resistant filaments available.
Printing Requirements
PC requires a heated bed (100–120°C) and an enclosed printer to prevent warping. Without an enclosure, PC parts are prone to cracking due to rapid cooling. When printed correctly, PC has strong layer adhesion and can produce very strong, durable parts.
Real-World Application
PC is often used for high-temperature applications like under-the-hood automotive components, electrical housings, and durable protective casings.
PETG – The Practical Strong Option
Why PETG is So Popular
PETG balances strength, ease of printing, and chemical resistance. It is often chosen for users who need strong parts but do not have an advanced printer or want to avoid high-temperature printing challenges.
PETG offers a combination of toughness and flexibility that makes it resistant to cracking under stress, while still being easy to print.
Key Properties
- Tensile Strength: 45–55 MPa
- Heat resistance: 70–80°C
- Good impact resistance
- Easy printing
- Good chemical resistance (acids and alcohols)
Mejores casos de uso
PETG is great for functional prototypes, outdoor parts, and mechanical components with moderate stress. Typical applications include:
- Outdoor fixtures and brackets
- Protective covers
- Enclosures for electronics
- Medium-load mechanical parts
Why PETG is Not the Absolute Strongest
While PETG is strong, it doesn’t match PC or carbon fiber nylon for extreme load and heat. It can deform under high temperatures and heavy continuous loads, which limits its use in high-performance engineering scenarios.
Real Data
PETG has a lower heat deflection temperature compared to PC and nylon, meaning it will soften earlier under heat. However, it is still stronger than PLA and provides a good balance between performance and ease of printing.
ABS – Tough, Heat Resistant, But Needs Skill
ABS Strength Profile
ABS is a classic engineering filament known for its toughness and heat resistance. It has been widely used in industrial manufacturing and consumer products for decades, largely due to its reliable mechanical properties.
ABS is a good choice for users who need durable parts and can handle the printing challenges.
Key Properties
- Tensile Strength: 40–50 MPa
- Heat resistance: 90–110°C
- Good toughness and impact resistance
- Moderate layer adhesion
- High stiffness under load
What Makes ABS a Strong Choice
ABS is durable and used in many industrial parts. It can handle impact and moderate heat better than PLA, and it is widely used in automotive and consumer electronics.
Printing Challenges
ABS requires an enclosed printing environment to avoid warping and cracking. It emits fumes during printing, so proper ventilation is necessary. Bed adhesion is critical, and a heated bed is required.
Real-World Example
Many automotive prototypes are printed with ABS due to its durability and toughness. ABS is also commonly used for functional enclosures and industrial housings.
Comparison Table – Which Filament is the Strongest?
| Material | Resistencia a la tracción (MPa) | Heat Resistance (°C) | Best Use Case | Difficulty |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Fiber Nylon | 50–70 | 120–140 | High-load mechanical parts | Hard |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | 60–70 | 150–160 | High-temp structural parts | Hard |
| PETG | 45–55 | 70–80 | General functional parts | Fácil |
| ABS | 40–50 | 90–110 | Tough prototypes | Medio |
Additional Insights: Strength Beyond Numbers

Why Layer Adhesion Matters More Than Filament Strength
A filament might have a high tensile strength, but if layers don’t bond well, the part can fail along the layer lines. Therefore, the strongest 3d printer filament is not just about material strength—it’s about overall print quality.
Why Print Settings Are Part of Strength
Even the strongest materials can fail if printed incorrectly. For example, carbon fiber nylon needs high temperatures and proper cooling. PC needs an enclosure. PETG needs correct flow settings to avoid stringing and weak layers.
How to Choose the Best “Strongest 3D Printer Filament”
Ask the Right Questions
- Will the part be under constant stress?
- Will it be exposed to heat or UV?
- Do you need flexibility or rigidity?
- Do you have a printer that supports high temperature printing?
Practical Decision Guide
- For maximum strength + heat resistance: choose PC
- For best strength-to-weight: choose carbon fiber nylon
- For easy and strong: choose PETG
- For toughness and low cost: choose ABS
Real-World Case Study
Industrial Use of Carbon Fiber Nylon
In manufacturing, carbon fiber nylon is used for drone frames, robotics parts, and heavy-duty brackets. A real company reported that replacing standard nylon with carbon fiber nylon increased part life by 35% under repeated stress.
Why PC is Used in Automotive
PC is used for headlight components, dashboard parts, and durable housings because it maintains strength at high temperatures and resists impact.
Expert Opinions & Literature Insights
What Engineers Say
Engineering professionals consider PC and carbon fiber nylon as the top strength filaments due to their engineering-grade performance.
Literature Reference
A 2022 materials study found that carbon fiber reinforcement increases tensile strength by 20–40% compared to pure nylon.
Final Thoughts
Choosing the strongest 3d printer filament depends on your application. If you want the best all-around strength, PC and carbon fiber nylon are top choices. For everyday strong parts, PETG is a great option.
To get the best results, focus on correct printing settings, strong layer adhesion, and proper cooling and bed temperature.
PREGUNTAS FRECUENTES
What is the strongest 3d printer filament for functional parts?
For functional parts under load, carbon fiber nylon or PC is usually the best choice due to high strength and heat resistance.
Can PETG be considered the strongest filament?
PETG is strong for general use but not the absolute strongest. It’s a balance of strength and ease of printing.
Is ABS stronger than PLA?
Yes, ABS is generally stronger and more heat-resistant than PLA, but PLA is easier to print.
What filament should I use for a high-temperature environment?
Polycarbonate (PC) is best for high temperatures due to its high heat resistance.
Which filament has the best impact resistance?
PC and carbon fiber nylon both have excellent impact resistance, with PC often ranking highest.
Categorías de productos
- Piezas de válvulas
- Piezas de la bomba de agua
- Piezas de la caja de cojinetes
- Piezas de fundición a presión
- Productos para bombas de acero inoxidable
- Productos para bombas de hierro fundido
- Piezas de válvulas para automóviles
- Recambios para automóviles
- Piezas de válvulas para uso civil
- Piezas de bomba de vacío KF

