Is 3D Printed Casting the Future? Here’s Why It Might Be
Tabla de contenido
Introducción
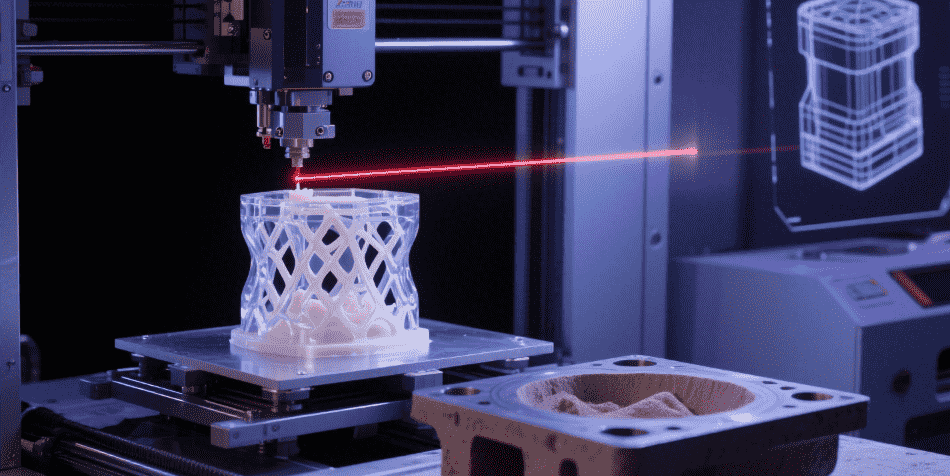
The casting industry has long been a cornerstone of manufacturing, providing reliable methods for producing metal components for a range of industries, from automotive to aerospace. Over the years, casting has evolved significantly with the introduction of new technologies aimed at improving speed, quality, and customization. One such innovation that is generating significant buzz is 3D printed casting. This cutting-edge technology leverages additive manufacturing to create molds or even final parts, opening up new possibilities for precision casting.
As industries look for ways to improve production efficiency and reduce waste, 3D printed casting presents itself as a potential game-changer. This blog will explore how this technology is disrupting traditional casting methods, the benefits it offers to manufacturers, and its potential to shape the future of precision casting. Additionally, we will discuss the challenges that still need to be overcome for its widespread adoption and consider its future prospects.
How 3D Printing is Revolutionizing the Casting Industry
3D printed casting represents a breakthrough in manufacturing, offering a method that replaces traditional molds and tooling with digital design files. This change allows for much greater design flexibility, faster production times, and reduced waste. Unlike traditional methods, which rely on creating molds from solid materials, 3D printed casting uses additive manufacturing to create complex structures that would otherwise be impossible or extremely expensive to produce.
The key advantage of 3D printed casting lies in its ability to create parts with intricate geometries, which traditional casting methods often struggle to produce. With additive technology, the part is built layer by layer, allowing for greater precision in even the most complicated designs.
Why This Technology Might Be the Future of Precision Casting
1. Increased Design Flexibility
One of the primary advantages of 3D printing in casting is its ability to offer unparalleled flexibility in part design. In traditional casting, the design is often limited by the mold’s constraints, including the need for cores and the inability to create intricate internal geometries. With additive manufacturing, these limitations are eliminated.
3D printing allows designers to create parts with complex geometries, including lattice structures, hollow chambers, and intricate internal channels, that would be challenging or impossible to achieve with conventional casting methods. This flexibility is particularly valuable in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where lightweight, high-performance parts are essential.
2. Faster Production and Shorter Lead Times
Speed is another significant advantage of 3D printing in casting. Traditional casting methods involve long lead times for the creation of molds, which can be particularly problematic in industries that demand quick turnaround times. With 3D printing, manufacturers can produce parts in a fraction of the time it would take to create a mold using traditional methods.
Because the design files are digital, manufacturers can quickly iterate on part designs and make adjustments without the time-consuming process of creating new molds. This reduction in production time can lead to faster prototyping and more efficient production, giving companies a competitive edge in industries with rapidly changing demands.
3. Reduced Costs and Material Waste
Cost savings are a major factor for many industries adopting 3D printed casting. Traditional casting often requires large quantities of material that may go to waste, especially when producing complex or custom parts. With 3D printed casting, material waste is significantly reduced since the process uses only the amount of material required for the part, layer by layer.
Additionally, 3D printed casting eliminates the need for expensive molds, which can significantly reduce upfront costs for small production runs or custom parts.
4. Improved Part Quality and Performance
By utilizing advanced materials such as metal powders and resins, 3D printing can produce parts that are not only more precise but also offer improved mechanical properties. Parts produced using additive manufacturing tend to have more consistent material properties, as the process minimizes the risk of defects that often occur with traditional casting methods.
3D printing also offers the ability to fine-tune material compositions, allowing manufacturers to optimize parts for specific performance criteria, such as strength, fatigue resistance, or corrosion resistance. This capability is particularly valuable in industries like aerospace, where performance and reliability are critical.
Applications of 3D Printed Casting in Precision Industries
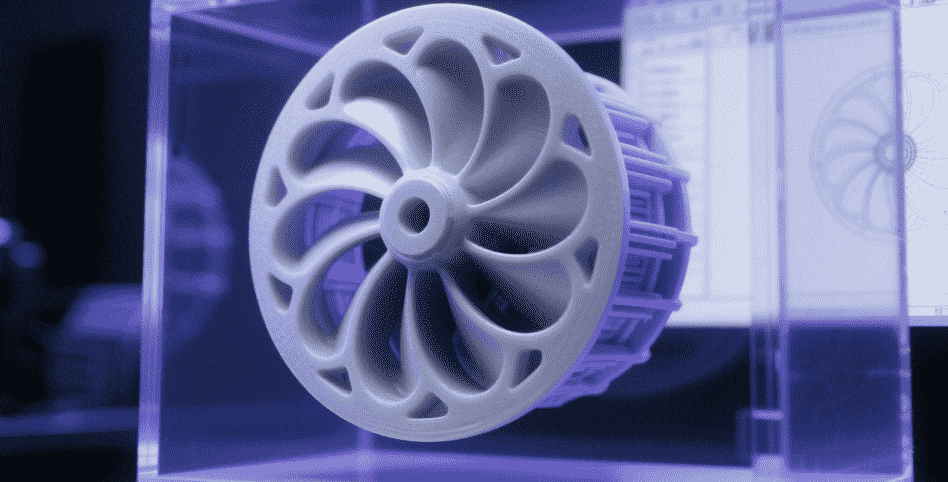
1. Industria aeroespacial
The aerospace sector is one of the biggest beneficiaries of 3D printed casting. Parts for aircraft often need to be lightweight but extremely strong, and 3D printing allows manufacturers to produce intricate parts that meet both of these criteria. With 3D printing, complex internal geometries, such as cooling channels or weight-saving lattice structures, can be incorporated into parts that were once impossible to produce with traditional casting techniques.
Moreover, aerospace manufacturers benefit from the quick turnaround times and reduced costs offered by 3D printing. The ability to rapidly prototype and produce small batches of custom parts allows manufacturers to adapt quickly to changes in design requirements, helping them maintain a competitive edge.
2. Industria automotriz
The automotive industry has also embraced 3D printing in casting due to the technology’s ability to produce lightweight components with complex shapes. 3D printed casting allows for the creation of custom parts that are both functional and innovative, whether for luxury vehicles or high-performance models. By reducing the weight of components, automakers can improve fuel efficiency and overall performance.
Additionally, manufacturers can quickly test new parts and designs, enabling faster innovation cycles and more efficient production processes. The ability to produce small runs of custom parts also opens up opportunities for vehicle personalization and specialized aftermarket components.
3. Medical Field
In the medical field, 3D printing in casting offers significant potential for creating custom implants, prosthetics, and surgical instruments. The precision and customization offered by the technology enable manufacturers to produce parts tailored to the specific needs of individual patients, improving patient outcomes and reducing recovery times.
Custom prosthetics, for instance, can be designed to fit the exact dimensions of a patient’s body, enhancing comfort and function. In addition to improving quality of life, 3D printed casting can also reduce the time and cost involved in producing these critical medical devices.
Challenges and Limitations of 3D Printed Casting
While the potential of 3D printing in casting is immense, there are still some challenges that need to be addressed for the technology to be fully integrated into the manufacturing mainstream.
1. Material Limitations
Mientras 3D printed casting offers many materials, the variety is still not as vast as that available for traditional casting. The types of metals and alloys that can be used in 3D printed casting are currently limited, although the situation is improving as technology evolves. In many cases, manufacturers may still need to rely on traditional casting for specific material requirements.
2. Size Limitations
Another limitation is the size of the parts that can be produced using 3D printing. Most 3D printers have size constraints that can limit their ability to produce larger components. For industries requiring large-scale parts, such as certain automotive or construction applications, traditional casting methods may still be more suitable.
3. Post-Processing Requirements
While 3D printed casting offers precision and speed, the parts often require post-processing to achieve the desired surface finish and mechanical properties. This additional step can add time and cost to the overall production process, although it can be minimized with advancements in 3D printing technology.
Table: Advantages of 3D Printing vs Traditional Casting
| Característica | Impresión 3D | Traditional Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibilidad de diseño | Alto | Limitado |
| Velocidad de producción | Rápido | Lento |
| Residuos de materiales | Bajo | Alto |
| Personalización | Fácil | Difícil |
| Cost for Small Runs | Bajo | Alto |
| Part Quality and Performance | Alto | Variable |
Conclusión
As industries continue to seek faster, more efficient, and cost-effective manufacturing methods, 3D printed casting stands out as a promising solution. The ability to create complex, customized parts quickly and at a lower cost makes this technology ideal for industries like aerospace, automotive, and healthcare.
Despite challenges like material limitations and the need for post-processing, the benefits of 3D printing in casting are undeniable. With continuous advancements in materials and techniques, we can expect this technology to play a major role in the future of precision casting, offering unprecedented opportunities for innovation and efficiency.
PREGUNTAS FRECUENTES
Q1: How does 3D printing improve part design compared to traditional casting?
A1: 3D printing allows for more complex geometries and intricate designs that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional methods. It offers greater flexibility and customization options.
Q2: What industries are benefiting from 3D printed casting?
A2: Industries such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare are seeing significant advantages from 3D printing due to its ability to create lightweight, high-performance parts with greater precision.
Q3: Are there any limitations to 3D printing in casting?
A3: Yes, material options are currently limited, and the size of the parts that can be produced is constrained. Additionally, post-processing may still be required to meet industry standards.
Q4: How does 3D printing reduce costs in casting?
A4: By eliminating the need for expensive molds and tooling, reducing material waste, and speeding up productiontimes, 3D printing helps lower costs, especially for custom or low-volume production.
Q5: Can 3D printed casting be used for large production runs?
A5: While 3D printing is ideal for small to medium runs, traditional casting methods may still be more cost-effective for large-scale production, though the gap is narrowing with improvements in 3D printing technology.
Manténgase conectado con nosotros

¡Gracias por leer! Esperamos que este blog te haya brindado información valiosa e inspiración sobre techos con paneles acústicos. Si disfrutaste del contenido y quieres estar al día de las últimas tendencias, consejos y novedades, nos encantaría conectar contigo en redes sociales.
📘 Síguenos en Facebook: Shanghai Leierwo Industria Comercio Co., Ltd.
Únase a nuestra creciente comunidad donde compartimos consejos de expertos, aspectos destacados de los productos y debates interactivos con profesionales y entusiastas del diseño de todo el mundo.
Sigamos conversando, ¡nos vemos allí!
Categorías de productos
- Piezas de válvulas
- Piezas de la bomba de agua
- Piezas de la caja de cojinetes
- Piezas de fundición a presión
- Productos para bombas de acero inoxidable
- Productos para bombas de hierro fundido
- Piezas de válvulas para automóviles
- Recambios para automóviles
- Piezas de válvulas para uso civil
- Piezas de bomba de vacío KF

