Fundición a la cera perdida vs. fundición en arena: 5 diferencias explicadas
When it comes to choosing the right casting process for a project, two of the most common methods are investment casting and sand casting. Both of these casting techniques have unique benefits and drawbacks depending on the complexity, material, and volume of parts being produced. In this article, we’ll dive into the key differences between fundición de precisión y fundición en arena to help you make an informed decision on which process is right for your application.
Tabla de contenido
Introducción
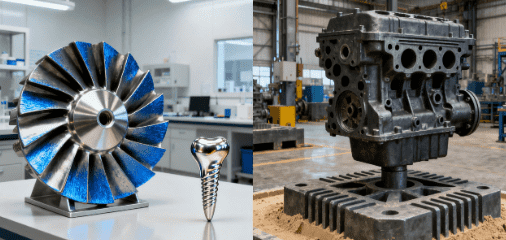
Before we dive into the differences, let’s first define fundición de precisión y fundición en arena. These are two of the most widely used casting methods in various industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and heavy equipment manufacturing.
- Fundición de inversión: Also known as lost-wax casting, investment casting involves creating a precise mold using a wax pattern. This process is known for producing parts with high accuracy and fine surface finishes. The mold is made by coating the wax pattern in a ceramic shell, and once hardened, the wax is melted out, leaving behind a hollow mold for pouring molten metal.
- Fundición en arena: Sand casting, on the other hand, uses sand to form the mold. The mold is created by packing sand around a pattern of the part to be cast, which is then removed, leaving behind a cavity that is filled with molten metal. Sand casting is a more cost-effective method for producing larger parts, but it does not offer the same level of detail or surface finish as investment casting.
In this article, we’ll explore five key differences between investment casting and sand casting, focusing on factors such as cost, accuracy, lead times, material compatibility, and applications.
Key Difference 1: Surface Finish and Dimensional Accuracy

Investment Casting vs Sand Casting: Which Provides Better Surface Finish?
One of the most significant distinctions between fundición de precisión y fundición en arena es el surface finish y dimensional accuracy of the parts produced. These factors often play a crucial role in determining which casting method is most appropriate for a given application.
Fundición de inversión
El fundición de precisión process, often referred to as lost-wax casting, results in parts with a smooth surface finish that typically requires minimal post-processing. The high-quality ceramic shell used to form the mold gives investment casting a significant advantage when it comes to surface quality. Because of this, fundición de precisión is widely used for complex geometries, intricate designs, and components that demand fine details and high surface quality. Parts produced by this method generally require less finishing work than parts produced by fundición en arena, which helps save time and labor costs.
The precision of fundición de precisión allows it to produce parts with smoother finishes that have significantly less visible texture, making it ideal for parts with exacting surface requirements, especially those used in industries like aerospace, medical devices, and electronics. The process’s ability to achieve high precision also means that it is capable of producing intricate micro-features that would otherwise be difficult to achieve with other casting methods.
Fundición en arena
In contrast, fundición en arena tends to leave parts with a rougher surface finish, requiring additional post-casting processes such as machining, grinding, o shot blasting to meet required tolerances. The mold itself is made of compacted sand, which leads to a more textured surface. This roughness can introduce challenges, such as porosity (tiny holes or voids), which may affect the mechanical properties or the aesthetic appearance of the final part. While fundición en arena is sufficient for many industrial applications, it’s not generally suitable for parts requiring fine surface finishes without significant post-processing work.
Moreover, the surface finish can also be affected by the choice of sand used, the molding process, and the complexity of the design. Sand casting is a more viable option for parts where roughness is acceptable or where the parts are relatively simple and do not require high cosmetic quality.s.
Dimensional Accuracy Comparison
- Fundición de inversión typically offers superior dimensional accuracy, with parts produced to tolerances as tight as ±0.005 inches (0.13mm). This level of precision makes it ideal for applications that require complex geometries and parts with high-performance standards, such as those found in the aerospace y medical industries. Due to the high precision, fundición de precisión can often eliminate the need for machining or other secondary processes.
- Fundición en arena, by comparison, has more lenient tolerances, typically ranging from ±0.015 to ±0.050 inches (0.38mm to 1.27mm), depending on the size and complexity of the part. While this may be acceptable for many industrial components, fundición en arena falls short when it comes to parts that demand highly detailed and precise design specifications. For high-precision applications, fundición de precisión is often the preferred choice due to its superior dimensional accuracy.
In general, if your project requires parts with fine surface finishes y tolerancias estrictas, fundición de precisión will likely be the better option. On the other hand, fundición en arena is a solid choice for applications where cost-efficiency is prioritized and surface finish and tolerances can be less critical.
Key Difference 2: Cost and Production Volume

Cost of Investment Casting vs Fundición en arena
Cost is often one of the most important factors to consider when deciding between fundición de precisión y fundición en arena. While fundición de precisión is known for its precision and ability to handle complex designs, it is generally more expensive due to the nature of the process.
Fundición de inversión
The higher costs associated with fundición de precisión stem from the creation of the molds. These molds are typically made from wax patterns that are coated in a ceramic shell, which is then fired to create the final mold. The labor-intensive nature of the process, combined with the high-quality materials required (such as ceramics y wax), makes fundición de precisión more expensive. Additionally, the process requires multiple steps to complete, including wax injection, shell building, y wax removal, all of which contribute to the cost.
Fundición de precisión is often more appropriate for small to medium production runs de high-precision parts, particularly when the requirements for detail y performance outweigh the importance of cost.
Fundición en arena
In contrast, fundición en arena es far more cost-effective, especially for large parts or high-volume production runs. The molds are created using a relatively inexpensive material—sand—combined with a binder to help shape it. Because the materials are low-cost and the process is less labor-intensive, fundición en arena is typically more affordable. Moreover, fundición en arena molds can be reused multiple times, further reducing costs for high-volume production.
Para larger parts o producción en masa, fundición en arena is usually the preferred method because it offers significant cost savings compared to fundición de precisión. However, when high precision y fine detailing are required, fundición de precisión will still be the go-to choice despite the higher cost.
Production Volume Considerations
- Fundición de inversión is ideal for low to medium production runs, especially when high precision is required. However, due to the higher tooling and labor costs, fundición de precisión becomes less cost-effective for large-volume production.
- Fundición en arena is well-suited for high-volume manufacturing, especially of larger parts that do not require the fine accuracy and high finish associated with fundición de precisión. The cost-efficiency de fundición en arena makes it a top choice for applications like engine blocks, large housings, y heavy-duty components.
Key Difference 3: Material Options
Material Compatibility in Investment Casting vs Fundición en arena
Ambos fundición de precisión y fundición en arena offer a broad range of materials, but the material choices available for each process vary in terms of compatibility, cost, and performance characteristics.
Fundición de inversión
Fundición de precisión allows for a broader selection of materials, including high-performance alloys y specialized metals. The process can accommodate materials such as acero inoxidable, aluminum, bronze, brass, y superalloys (such as titanium, nickel-based alloys, y cobalt-based alloys). These metals are ideal for applications that require high strength, resistance to corrosion, or the ability to perform under extreme conditions. The fine detailing achievable in fundición de precisión makes it the go-to process for aerospace, medical, y automotive components that need specialized alloys with exacting properties.
Fundición en arena
Sand casting also offers a wide range of material options, although it is generally more limited in terms of specialized alloys. It is most commonly used with ferrous y non-ferrous metals such as gray iron, aluminum, bronze, y brass. While it can also be used for steel alloys, it is generally not as suitable for higher-performance materials like superalloys. The process is better suited for cast iron y aluminum alloys, making it more suitable for large, simpler parts used in industries like construction, heavy machinery, y automotive.
| Tipo de material | Fundición de inversión | Fundición en arena |
|---|---|---|
| Steel | Yes (including high-alloy steels) | Yes (standard carbon steel) |
| Aluminio | Yes | Yes |
| Bronze & Brass | Yes | Yes |
| Iron | Yes | Yes (including gray iron) |
| Titanio | Yes | Limitado |
Key Difference 4: Lead Time and Turnaround

Investment Casting vs Fundición en arena: Which Has a Shorter Lead Time?
When comparing the lead time y turnaround times of fundición de precisión y fundición en arena, it’s essential to consider the different complexities involved in each process.
Fundición de inversión
Fundición de precisión, while known for its precision, can have a longer lead time. This is primarily due to the intricate process of creating wax patterns, followed by coating them with a ceramic shell and allowing it to dry. The time required to produce these molds can be significant, especially for complex designs. The wax pattern creation process involves meticulous attention to detail to ensure that the final part matches the desired specifications.
However, once the molds are created, the casting process itself can be relatively quick. After the wax is melted out, the molten metal is poured into the mold, which is a much faster step. As a result, fundición de precisión is generally preferred for low to medium production runs o prototyping when precision y detail are critical, despite the longer initial mold creation time.
Fundición en arena
On the other hand, fundición en arena tends to have a shorter lead time compared to fundición de precisión, primarily because of its simpler mold-making process. Sand molds are created by compacting sand around a pattern, which is much faster than the intricate mold-making process of fundición de precisión. Additionally, sand molds can be reused, which further shortens lead times for repeat orders and high-volume productions.
Sand casting can often be completed more quickly for large parts o producción en masa runs, especially if the parts do not require highly detailed or complex features. It’s an excellent choice when fast turnaround is essential and when the focus is more on cost-effectiveness rather than precision.
In summary, if you are looking for fast lead times para large-volume production, fundición en arena is likely the better choice. However, if your project requires high precision y detailed designs, fundición de precisión will require a longer lead time but ultimately provide superior results.
Key Difference 5: Application Suitability
Which Casting Process Is Right for Your Application?
When deciding between fundición de precisión y fundición en arena, it’s essential to consider which process is best suited for the requirements of your specific application. Both casting methods have their strengths, but the decision depends on factors such as part complexity, volume, and performance needs.
Fundición de inversión
Fundición de precisión is ideal for parts that require high precision, intricate designs, y tolerancias estrictas. Its ability to produce complex geometries with detailed features makes it a top choice for industries that demand high-performance parts.
- Aeroespacial: For producing lightweight, high-strength components like turbine blades, fundición de precisión ensures both precision y performance under extreme conditions.
- Automotor: When manufacturing components like engine blocks, valves, o turbochargers, fundición de precisión is used for its ability to produce highly detailed y complex parts that require durability and strength.
- Dispositivos médicos: The need for fine details, biocompatibility, y precision in components like surgical tools o prosthetics makes fundición de precisión the go-to method.
- Energy: Critical components such as valves, seals, y turbines benefit from the superior precision and material versatility offered by fundición de precisión.
Given the nature of these industries, fundición de precisión is often the best choice when high performance y precision are required, particularly for low to medium volume runs de complex parts.
Fundición en arena
Mientras fundición de precisión excels in precision, fundición en arena is typically more suited for larger, less complex parts. This casting method is ideal for parts where cost-efficiency is a top priority, and the parts don’t require the level of detail o precision that fundición de precisión provides.
- Construcción: Sand casting is widely used for producing large, simple components like manhole covers, construction machinery parts, y heavy-duty castings.
- Heavy Machinery: Components that require strength but don’t need fine surface finishes, such as engine blocks y gear housings, can be effectively manufactured using fundición en arena.
- Equipos industriales: Parts that need to be both functional y cost-effective, like pumps, valves, y bearing housings, are often produced using fundición en arena because of its low material costs and efficiency for large production runs.
For industries where producción en masa y cost efficiency are more critical than fine detailing, fundición en arena offers a practical solution. This method is ideal for larger parts o high-volume production de simple geometries that do not require precision machining o tolerancias estrictas.
Conclusión
In conclusion, both fundición de precisión y fundición en arena have their place in the manufacturing world. The right choice depends on factors like material type, production volume, cost constraints, and the precision required for the part. Fundición de precisión shines when high accuracy and detailed surface finishes are required, whereas fundición en arena remains the go-to method for large, simpler parts that prioritize cost-effectiveness.
By understanding the key differences between investment casting and sand casting, you can select the casting process that best meets the specific needs of your project, ensuring both quality y efficiency.
PREGUNTAS FRECUENTES
1. Which process is better for large parts?
Sand casting is typically the better option for producing large parts. The sand molds can be easily scaled to accommodate bigger components, and the process is more cost-effective for mass production. Sand casting is often the go-to method for industries that require large, simple shapes in bulk.
2. Es fundición de precisión suitable for high-volume production?
Fundición de precisión is generally better suited for low to medium-volume production due to its higher cost. However, for specialized parts that require high precision and complex geometries, investment casting can be used effectively in high-volume applications where accuracy justifies the additional cost.
3. Can investment casting be used for intricate designs?
Sí, fundición de precisión excels at producing intricate designs and parts with complex geometries. The precision of the process allows for the creation of fine details and tight tolerances, making it ideal for applications in industries like aerospace and medical devices.
4. Which process is better for prototyping?
Fundición de precisión is often the preferred method for prototyping, especially when high accuracy y functional prototypes are needed quickly. The process allows for rapid creation of detailed and dimensionally accurate prototypes, enabling efficient testing and adjustments.
5. Can fundición en arena achieve tight tolerances?
Sand casting typically does not offer the same level of precision as fundición de precisión and is best suited for parts with moderate tolerances. While it can still produce functional parts with reasonable accuracy, it generally requires additional finishing to meet tight tolerance specifications.
Manténgase conectado con nosotros

¡Gracias por leer! Esperamos que este blog te haya brindado información valiosa e inspiración sobre techos con paneles acústicos. Si disfrutaste del contenido y quieres estar al día de las últimas tendencias, consejos y novedades, nos encantaría conectar contigo en redes sociales.
📘 Síguenos en Facebook: Shanghai Leierwo Industria Comercio Co., Ltd.
Únase a nuestra creciente comunidad donde compartimos consejos de expertos, aspectos destacados de los productos y debates interactivos con profesionales y entusiastas del diseño de todo el mundo.
Sigamos conversando, ¡nos vemos allí!
Categorías de productos
- Piezas de válvulas
- Piezas de la bomba de agua
- Piezas de la caja de cojinetes
- Piezas de fundición a presión
- Productos para bombas de acero inoxidable
- Productos para bombas de hierro fundido
- Piezas de válvulas para automóviles
- Recambios para automóviles
- Piezas de válvulas para uso civil
- Piezas de bomba de vacío KF

