Lightweight Engine Cylinder Blocks: Casting Insights
Willkommen auf meinem Blog!
Ich freue mich sehr, dass du hier bist! Bevor wir uns in die Inhalte vertiefen, würde ich mich freuen, wenn du mir auf meinen Social-Media-Plattformen folgst. Dort teile ich zusätzliche Einblicke, vernetze mich mit unserer großartigen Community und halte dich über die neuesten Nachrichten auf dem Laufenden. So bleibst du in Verbindung:
📘 Facebook: Shanghai Leierwo Industriehandel Co., Ltd.
Lassen Sie uns gemeinsam auf diese Reise gehen! Ich hoffe, Sie finden die Inhalte hier nicht nur aufschlussreich, sondern auch inspirierend und wertvoll. Los geht‘s!
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Key Takeaways
- Comprehensive exploration of lightweight engine cylinder block materials and casting methods.
- Detailed comparison of cast iron, aluminum alloys, and composite blocks.
- Insights into sand casting, high-pressure die casting, and lost foam casting.
- Advanced design considerations: thermal management, stress distribution, surface treatment.
- Performance metrics, durability studies, and industry case studies.
- FAQ addressing common engineering and maintenance concerns.
Understanding Lightweight Engine Cylinder Blocks

What is an Engine Cylinder Block?
The engine cylinder block is the structural heart of an internal combustion engine, housing cylinders, coolant passages, oil galleries, and, in most cases, the crankcase. Traditionally, blocks are made from cast iron due to its durability and wear resistance. However, the modern automotive and industrial landscape increasingly favors lighter alternatives to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
Why Lightweight Matters
Reducing engine mass contributes to:
- Improved fuel economy: Each 10% reduction in engine weight can improve overall vehicle fuel efficiency by 3–5%.
- Better handling and acceleration due to lower inertia.
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions in line with global regulatory trends.
Lightweight engine cylinder blocks have become central to modern vehicle design, particularly in electric and hybrid vehicles where efficiency gains are crucial.
Materials Used in Lightweight Engine Cylinder Blocks
Aluminiumlegierungen
Aluminum alloys are widely adopted for their high strength-to-weight ratio and superior thermal conductivity.
Key Properties:
- Density: ~2.7 g/cm³ (vs. cast iron ~7.2 g/cm³).
- Thermal conductivity: 150–200 W/m·K, enhancing cooling efficiency.
- Yield strength: 200–400 MPa depending on alloy and heat treatment.
Vorteile:
- Reduces engine weight by up to 40%.
- Better thermal efficiency supports higher compression ratios.
Limitations:
- Susceptible to wear without coatings like Nikasil.
- Requires precise casting methods to avoid porosity or shrinkage defects.
Brancheneinblicke:
According to Dr. John F. Smith, Head of Powertrain Materials at SAE International, “Aluminum cylinder blocks, when properly treated and cast, can match or exceed the fatigue life of traditional cast iron in high-performance engines.”
Composite Materials
Emerging composite blocks combine metals with ceramic or polymer reinforcements to optimize weight, thermal management, and vibration damping.
Vorteile:
- Potential 50% or more weight reduction relative to cast iron.
- Customizable thermal expansion coefficients for high-performance engines.
Limitations:
- High manufacturing costs limit widespread adoption.
- Industrial scalability remains a challenge for mass production.
Material Comparison: Cast Iron vs. Aluminum vs. Composite
| Besonderheit | Gusseisen | Aluminum Alloy | Composite |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dichte | 7.2 g/cm³ | 2.7 g/cm³ | 1.8–2.2 g/cm³ |
| Thermal Conductivity | 50 W/m·K | 150–200 W/m·K | 100–180 W/m·K |
| Verschleißfestigkeit | Exzellent | Mäßig | Varies (reinforced) |
| Bearbeitbarkeit | Gut | Mäßig | Mäßig |
| Kosten | Niedrig | Medium | Hoch |
| Weight Reduction Potential | Baseline | 30–40% | 50–60% |
This table highlights the trade-offs engineers must consider when selecting block materials based on performance, cost, and manufacturing feasibility.
Casting Techniques for Lightweight Engine Cylinder Blocks
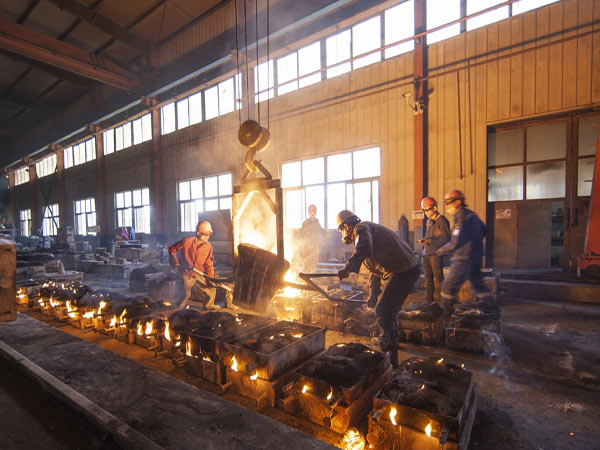

Sandguss
Sand casting remains a versatile and cost-effective method, especially for prototypes and small production runs. Aluminum and some composite blocks can be produced with fine-grain silica sand molds.
Vorteile:
- Good for complex geometries and variable wall thickness.
- Lower initial tooling costs.
Limitations:
- Surface finish may require extensive machining.
- Porosity control is critical for high-strength aluminum alloys.
Fallstudie:
A European manufacturer produced a 4-cylinder aluminum prototype block using high-quality silica sand. Results: wall thickness tolerance ±0.5 mm, minimal shrinkage defects, ready for machining and surface treatment.
High-Pressure Die Casting (HPDC)
HPDC involves injecting molten aluminum into steel dies at high pressure, ideal for high-volume production of aluminum blocks.
Vorteile:
- Excellent dimensional accuracy (<0.2 mm).
- Smooth surfaces reduce post-casting machining.
- High repeatability suitable for mass production.
Herausforderungen:
- High die cost (~$100k–$300k per die for full engine block).
- Limited ability to produce thick sections or highly variable geometries.
Data Insight:
According to the International Aluminum Institute, HPDC aluminum engine blocks can achieve a density reduction of 40% while maintaining 95% of the compressive strength of equivalent cast iron blocks.
Lost Foam Casting
Lost foam casting offers precise reproduction of complex shapes and is increasingly used for lightweight blocks with thin walls.
Vorteile:
- Minimal machining required.
- Thin walls enable maximum weight reduction.
Limitations:
- Highly sensitive to pouring rates and mold quality.
- Requires skilled operators and tight process control.
Industry Adoption:
Ford Motor Company reported using lost foam casting for certain EcoBoost engine blocks, reducing weight by 35% and maintaining durability for over 200,000 km of road testing.
Modern Design Considerations
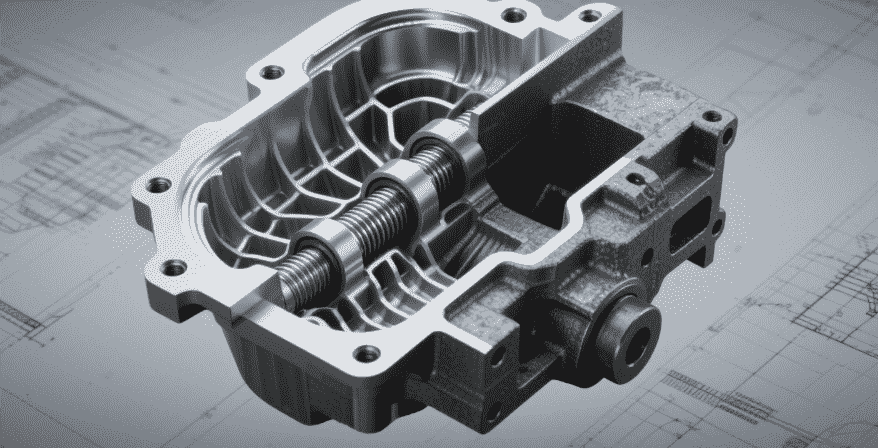
Cooling and Thermal Management
Thermal management is critical for aluminum and composite blocks due to higher thermal expansion compared to cast iron. Engineers often integrate:
- Optimized coolant channels with uniform flow distribution.
- Localized heat sinks or fins to reduce hot spots.
- CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) simulations to predict temperature gradients.
Strength vs. Weight Trade-Off
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is used to simulate stresses under combustion loads. Critical design elements include:
- Reinforced rib structures to reduce flexing.
- Strategic material distribution around cylinder walls.
- Integration of structural inserts or sleeves for wear resistance.
Surface Treatment & Coating
Aluminum blocks often undergo:
- Nikasil or Alusil coatings for cylinder walls to reduce wear.
- Thermal spray or plasma coatings to improve corrosion resistance.
- Micro-shot peening to relieve residual stresses and extend fatigue life.
Comparing Lightweight Cylinder Blocks to Traditional Designs
Performance Metrics
- Weight Reduction: Aluminum reduces engine block mass by 30–40%; composites up to 50%.
- Fuel Efficiency Gains: Lighter engines can improve vehicle fuel economy by 5–10%.
- Thermal Conductivity: Aluminum blocks dissipate heat faster, reducing hotspots by 15–20°C under high-load testing.
Durability and Maintenance
While aluminum and composites reduce weight, cast iron remains superior in extreme high-wear applications. Surface treatments and proper lubrication are essential for maintaining durability.
Cost Considerations
- Initial casting cost: HPDC > Lost Foam > Sand Casting.
- Long-term operational cost savings: Aluminum/composite blocks reduce fuel consumption, potentially offsetting higher production costs over vehicle lifespan.
Advanced Engineering and Quality Control
Maßgenauigkeit
Modern blocks require tolerances as tight as ±0.1 mm for cylinder bores. Non-destructive testing methods include:
- X-ray radiography to detect porosity and cracks.
- Ultrasonic testing for internal defects.
- Laser scanning for surface geometry verification.
Fatigue and Vibration Analysis
Engineers simulate load cycles to ensure blocks withstand thermal expansion, combustion pressures (~100–150 bar), and engine vibrations (>30,000 cycles per hour).
Metallurgical Insights
- Microstructure control: Grain refinement improves strength and reduces casting defects.
- Alloying elements: Si, Cu, Mg, and Ni balance strength, wear resistance, and machinability.
- Heat treatment: T6 and T7 processes improve tensile strength and fatigue life.
Fallstudien aus der Praxis
High-Performance Automotive Engines
- BMW B58 Aluminum Block: 6-cylinder inline engine using HPDC aluminum block with Nikasil coating. Weight reduction: ~35 kg vs. previous cast iron. Thermal efficiency improved by 5%.
- Ford EcoBoost 1.5L I3: Lost foam aluminum block with integrated structural ribs. Weight reduction: 28%, improved fuel efficiency by 7%.
Industrial Engine Applications
- Caterpillar C7 ACERT engine: Aluminum cylinder block with composite cylinder liners. Achieves comparable durability to cast iron while reducing weight for transport and fuel efficiency.
Abschluss
Lightweight engine cylinder blocks represent the forefront of modern engine design. By selecting appropriate materials, casting methods, and surface treatments, engineers can produce blocks that are lighter, more thermally efficient, and durable. Aluminum and composite blocks provide:
- Weight reductions up to 50%.
- Improved fuel efficiency and thermal management.
- Viable performance in both automotive and industrial engines.
Advanced casting techniques such as HPDC, lost foam, and precision sand casting, combined with simulation-driven design and quality control, enable consistent, high-performance production. As emissions standards tighten and fuel efficiency becomes critical, lightweight engine cylinder blocks will be central to future engine technologies.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Q1: What is the primary benefit of a lightweight engine cylinder block?
A: Reduced weight improves fuel efficiency, handling, and reduces emissions without sacrificing performance when designed properly.
Q2: Are aluminum or composite blocks durable enough for performance engines?
A: Yes. With proper casting, machining, and coatings, they match or exceed cast iron durability in modern engines.
Q3: How does casting method affect performance?
A: Casting impacts dimensional accuracy, porosity, surface finish, and heat transfer. HPDC and lost foam methods provide higher precision for lightweight aluminum blocks.
Q4: Can cast iron blocks be retrofitted with lightweight materials?
A: No. Lightweight blocks must be designed from the start with aluminum or composites due to different mechanical properties and thermal expansion.
Q5: Which is better for cost-sensitive projects?
A: Cast iron has lower upfront costs, but aluminum and composites offer long-term fuel savings and reduced emissions, often offsetting initial costs.
Q6: How do coatings enhance block lifespan?
A: Coatings like Nikasil or Alusil reduce wear, improve heat transfer, and allow aluminum blocks to endure high-pressure, high-temperature conditions.
Produktkategorien
- Ventilteile
- Wasserpumpenteile
- Lagergehäuseteile
- Druckgussteile
- Pumpenprodukte aus Edelstahl
- Pumpenprodukte aus Gusseisen
- Ventilteile für den Automobilgebrauch
- Autoteile
- Ventilteile für den zivilen Gebrauch
- Vakuumpumpenteile KF

