7 Powerful Tips for Cast Iron vs Stainless Steel in Casting
مرحباً بكم في مدونتي!
يسعدني وجودك هنا! قبل أن نتعمق في المحتوى، أود أن تنضموا إليّ على منصات التواصل الاجتماعي. هناك أشارككم أفكارًا إضافية، وأتواصل مع مجتمعنا الرائع، وأُطلعكم على آخر الأخبار. إليكم كيفية البقاء على تواصل:
📘 فيسبوك: شركة شنغهاي لييروو الصناعية التجارية المحدودة
الآن، لننطلق في هذه الرحلة معًا! آمل أن تجدوا هذا المحتوى مفيدًا ومُلهمًا وقيّمًا. هيا بنا!
جدول المحتويات
مقدمة
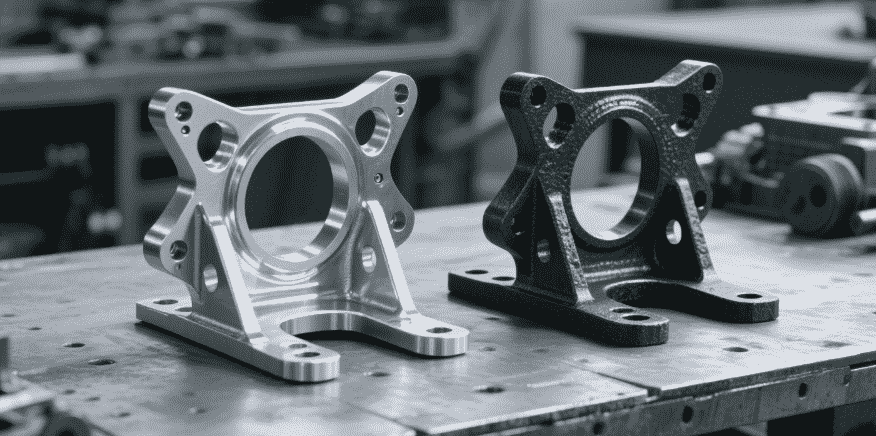
In the fast-paced world of industrial casting, selecting the right material is more than a technical decision—it can determine the success or failure of your project. Engineers and foundry managers constantly face the challenge of choosing between cast iron vs stainless steel, both of which have unique properties, advantages, and limitations.
Cast iron is prized for its high compressive strength, wear resistance, and heat retention. Stainless steel, on the other hand, offers superior corrosion resistance, aesthetic finish, and tensile strength. According to a 2023 report from the Foundry Industry Association, nearly 35% of component failures in industrial applications were traced back to poor material selection, highlighting the importance of making an informed choice.
This blog aims to guide professionals through seven powerful tips for optimizing casting decisions between cast iron vs stainless steel, providing detailed comparisons, data-driven insights, and expert recommendations for long-term performance and cost efficiency.
Tip 1: Assessing Mechanical and Physical Properties of Cast Iron vs Stainless Steel
Mechanical and physical properties are the foundation for material selection. Cast iron has high compressive strength (250–400 MPa) and moderate hardness, making it ideal for static loads and machinery bases. Stainless steel has high tensile strength (500–750 MPa), ductility, and excellent corrosion resistance, suitable for dynamic and chemically aggressive environments. Factors such as impact resistance, fatigue strength, and wear characteristics should be evaluated.
الاعتبارات الرئيسية
- Impact of cyclic and dynamic loads
- Surface treatment and wear resistance
- Material brittleness and deformation under stress
Expert Insight
Dr. Jonathan Reynolds, metallurgical engineer at MetalWorks Research, states, “Cast iron is excellent for load-bearing applications, but stainless steel’s ductility and corrosion resistance make it indispensable in modern industrial design.”
Tip 2: Corrosion Resistance and Longevity Comparison
Corrosion resistance is a major differentiator. Cast iron is prone to oxidation and requires protective coatings. Stainless steel grades such as 304 and 316 offer long-term resistance in harsh environments. Selecting the appropriate material based on exposure ensures durability and reduces maintenance costs.
Factors Affecting Corrosion
- Moisture and humidity
- Acidic or alkaline exposure
- High-temperature operation
- Chemical contact during processing
- Salt or marine environments
Data Insight
A 2022 study by the International Journal of Materials Science found that stainless steel components lasted up to 15 years longer than untreated cast iron in high-humidity industrial environments.inimizes downtime.
Tip 3: Thermal Properties and Heat Management
Thermal management is critical in casting. Cast iron has high thermal conductivity (50–80 W/m·K) and retains heat efficiently, making it ideal for engine blocks, cookware, and heat exchangers. Stainless steel has moderate thermal conductivity (15–25 W/m·K) but maintains stability under thermal cycling without deformation.
Case Study
An industrial furnace manufacturer switched from cast iron to stainless steel for heat-sensitive parts. Initial costs increased by 20%, but maintenance downtime decreased by 35%, illustrating the importance of thermal considerations in material selection.
Tip 4: Cost Analysis – Upfront vs Long-Term
Cast iron is generally cheaper initially, but stainless steel offers better long-term value due to lower maintenance and longer lifespan.
Cost Factors
- Initial material and manufacturing costs
- Maintenance frequency
- Expected lifespan
- Energy efficiency and thermal performance
Comparison Table
| عامل | الحديد الزهر | الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ |
|---|---|---|
| Material Cost | قليل | عالي |
| Manufacturing Complexity | معتدل | عالي |
| Maintenance Requirement | Medium (coating/painting) | Low (minimal maintenance) |
| Lifespan | 10–15 years | 20–25 years |
| Energy Efficiency | High thermal retention | Moderate thermal efficiency |
Tip 5: Casting Techniques and Process Optimization
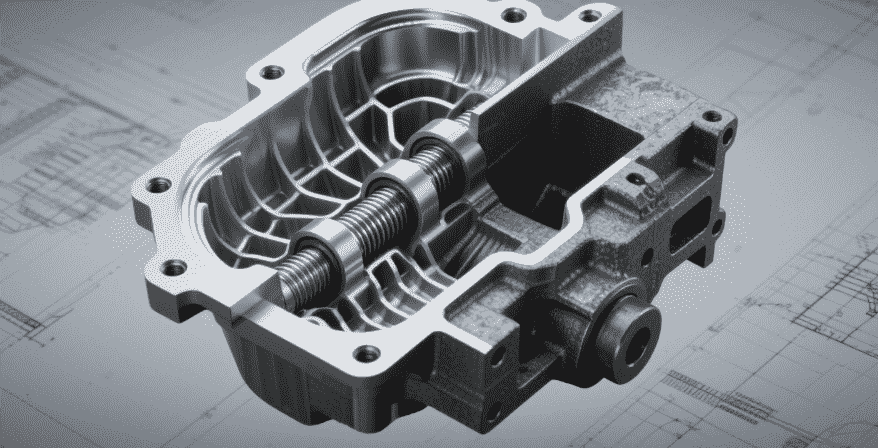
The casting processes differ between cast iron vs stainless steel. Cast iron’s high fluidity allows intricate shapes and is less sensitive to mold temperature. Stainless steel requires precise mold design, controlled cooling, and monitoring to reduce porosity and surface defects.
أفضل الممارسات
- Verify mold material compatibility
- Control pouring and cooling rates
- Conduct trial runs for complex geometries
- Inspect for shrinkage and porosity
Expert Tip
Dr. Maria Lopez, senior metallurgist at Global Casting Solutions, notes, “Optimizing mold design and cooling rates for stainless steel can significantly reduce defect rates, improving component reliability.”
Tip 6: Applications and Industry-Specific Considerations
Knowing where each material excels is crucial. Cast iron is preferred for engine blocks, pump housings, industrial valves, and heavy machinery bases. Stainless steel is ideal for food processing, chemical plants, medical devices, and high-hygiene piping.
Industry Insights
- Automotive: cast iron for durability, stainless steel for exhaust and corrosion-prone parts
- Food processing: stainless steel for hygiene and chemical resistance
- Heavy machinery: cast iron for vibration damping and wear resistance
Survey Data
A 2021 American Foundry Society survey reported 62% of foundries used stainless steel for chemical applications, while 58% relied on cast iron for engines and machinery.
Tip 7: Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
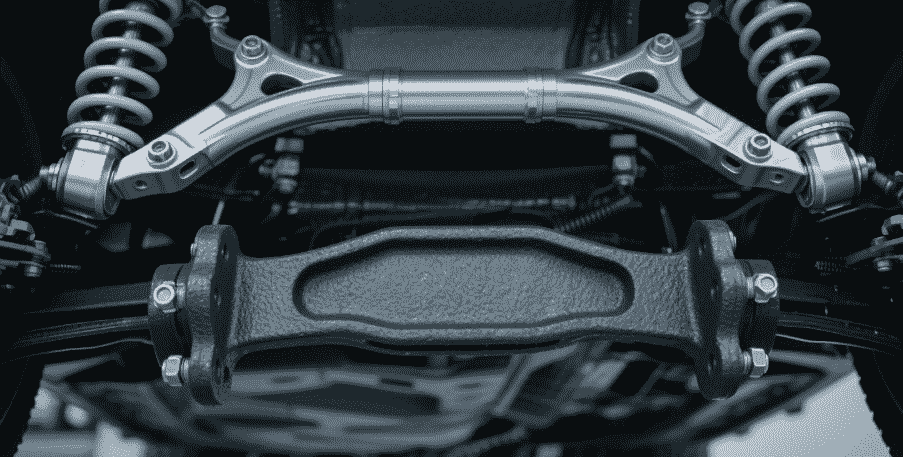

Regulatory compliance guarantees safety, performance, and legality. Standards such as ASTM, ISO, and FDA (for food/medical use) must be followed. Verifying mechanical properties, corrosion testing, and hygienic compliance reduces failure risk.
Compliance Checklist
- ASTM or ISO certification verification
- FDA or hygiene standards for stainless steel
- Pressure, thermal, and corrosion resistance testing
- Traceability of raw materials
Lifecycle Considerations
- Plan maintenance schedules for cast iron coatings
- Use stainless steel to reduce repair frequency
- Consider hybrid approaches combining cast iron and stainless steel for cost-effectiveness and performance
Additional Tips and Expert Insights
- Tip 8: Perform sample casting and prototype testing for both materials.
- Tip 9: Consult with suppliers on material innovations like duplex stainless steel or alloyed cast iron.
- Tip 10: Monitor operational environment continuously; humidity and chemical exposure can alter material choice mid-project.
Expert Quote:
Dr. Eric Thompson, Director of Materials Research at TechMetals, says, “The choice between cast iron vs stainless steel isn’t always binary; hybrid approaches using both materials can optimize performance and cost.”
الأسئلة الشائعة
Q: Which is better for outdoor industrial machinery?
A: Stainless steel is preferable due to corrosion resistance, though coated cast iron may be suitable for non-critical parts.
Q: Can cast iron be alloyed to improve performance?
A: Yes, adding chromium, molybdenum, or nickel can enhance hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion protection.
Q: How does thermal cycling affect stainless steel vs cast iron?
A: Stainless steel tolerates repeated heating and cooling with minimal deformation; cast iron may crack under extreme thermal cycling.
Q: Is stainless steel always the most cost-effective choice?
A: Not always. While it reduces maintenance, higher upfront costs may not be justified for non-critical or dry applications.
Q: What tests should I perform before full-scale casting?
A: Pressure tests, corrosion tests, and dimensional inspections are essential for both cast iron and stainless steel components.
Q: Are there hybrid solutions combining cast iron and stainless steel?
A: Yes, some applications use cast iron bases with stainless steel contact surfaces to optimize strength and corrosion resistance simultaneously.
خاتمة
Selecting the right material between cast iron vs stainless steel in casting requires a holistic evaluation of mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, thermal behavior, cost, compliance, and application requirements. Following the seven (plus additional) tips outlined in this blog ensures engineers, manufacturers, and procurement teams make informed, data-driven decisions.
By carefully balancing cost, performance, longevity, and environmental considerations, smart buyers can optimize casting outcomes, reduce maintenance, and achieve long-term efficiency in industrial projects. Remember, success in casting is not just about choosing a material; it’s about understanding the nuances of each material and how it aligns with your operational goals.
فئات المنتجات
- أجزاء الصمامات
- أجزاء مضخة المياه
- أجزاء صندوق المحمل
- أجزاء الصب بالقالب
- منتجات مضخات الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ
- منتجات مضخات الحديد الزهر
- قطع غيار الصمامات لاستخدام السيارات
- قطع غيار السيارات
- أجزاء الصمامات للاستخدام المدني
- قطع غيار مضخة التفريغ KF

