Thermoplastic Polyolefin: Must-Have Material Insights
Welcome to My Blog!
I’m thrilled to have you here! Before we dive into the content, I’d love for you to join me on my social media platforms. It’s where I share extra insights, connect with our amazing community, and keep you updated on the latest news. Here’s how you can stay connected:
📘 Facebook: Shanghai Leierwo Industry Trade Co., Ltd.
Now, let’s embark on this journey together! I hope you find the content here not only insightful but also inspiring and valuable. Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving world of 3D printing, materials play a pivotal role in determining the quality, durability, and functionality of the final products. Among the diverse materials available, thermoplastic polyolefin has emerged as a must-have option for 3D printing casting applications. Known for its exceptional chemical resistance, dimensional stability, and process adaptability, thermoplastic polyolefin is increasingly preferred by engineers and manufacturers who demand precision and performance.
3D printing casting requires materials that can endure post-processing operations such as sintering, molding, or finishing. Traditional polymers often fall short due to shrinkage, brittleness, or poor surface finish. Thermoplastic polyolefin addresses these challenges, offering a combination of flexibility, strength, and resistance to deformation under heat and pressure.
This article explores the key properties, applications, advantages, and considerations of thermoplastic polyolefin in the context of 3D printing casting, providing an essential resource for designers, manufacturers, and procurement specialists.
Key Properties of Thermoplastic Polyolefin in 3D Printing
Understanding the material properties of thermoplastic polyolefin is crucial for optimizing 3D printing casting workflows. Its unique combination of mechanical strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance makes it an excellent choice for a wide range of casting applications. By leveraging these properties, engineers and manufacturers can improve part quality, reduce production errors, and streamline post-processing.
Chemical Resistance

Thermoplastic polyolefin exhibits outstanding resistance to a variety of chemicals, including acids, bases, and solvents. This property is particularly important for molds and castings that may come into contact with harsh substances during production or end-use. Its chemical resilience ensures that molds do not degrade or react, maintaining surface integrity and dimensional accuracy throughout repeated casting cycles.
Thermal Stability
One of the critical challenges in 3D printing casting is maintaining dimensional precision under varying thermal conditions. Thermoplastic polyolefin excels in this area by retaining its shape and mechanical properties even under elevated temperatures. This thermal stability reduces the risk of warping or shrinkage, which is essential for producing highly accurate prototypes, functional parts, and mold inserts.
Flexibility and Toughness
Unlike many brittle polymers that crack or fracture under mechanical stress, thermoplastic polyolefin combines toughness with flexibility. It can absorb significant mechanical stress without failing, which reduces the likelihood of damage during post-processing or handling. This property is particularly beneficial in complex parts where stress points are unavoidable, ensuring the durability of the final casting.
Surface Finish
The naturally smooth surface properties of thermoplastic polyolefin reduce the need for extensive finishing after printing. Parts produced with this material require minimal sanding, polishing, or coating, saving both time and labor costs. In applications such as mold inserts or investment casting patterns, a high-quality surface finish also contributes to better replication of details in the final casted product.
Process Adaptability
Thermoplastic polyolefin is compatible with multiple 3D printing technologies, including FDM, SLS, and resin-based casting methods. Its versatility allows engineers to choose the optimal printing method for their application, whether it’s rapid prototyping, small-batch production, or high-precision casting. The adaptability also makes it easier to integrate into hybrid manufacturing workflows that combine polymers with metals or ceramics.
Applications of Thermoplastic Polyolefin in 3D Printing Casting
Thermoplastic polyolefin has a broad range of applications in the 3D printing casting domain, especially where precision, durability, and post-processing efficiency are critical. By understanding how this material is used across industries, manufacturers can make informed decisions about its suitability for their specific workflows.
Investment Casting Patterns
One of the most common applications of thermoplastic polyolefin is in investment casting patterns. The material can be 3D-printed to produce precise, stable patterns that will later be replaced by metal or ceramic materials. Its dimensional accuracy and thermal resistance ensure that the final casting matches the intended design closely.
Mold Inserts
Thermoplastic polyolefin is also ideal for creating durable mold inserts. These inserts can withstand repeated use without significant wear, ensuring consistent quality across multiple production cycles. Its toughness and resistance to deformation make it a reliable material for high-volume casting operations.
Prototyping Complex Components
For companies developing complex parts, thermoplastic polyolefin enables rapid prototyping. Engineers can iterate designs quickly, testing functional features and fit without the high risk of material failure. Its ability to mimic the performance characteristics of final production materials provides valuable insights during the design stage.
Automotive Parts Casting
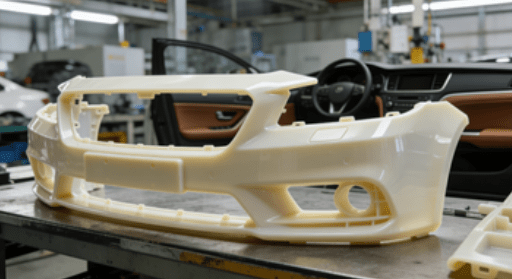
In the automotive industry, thermoplastic polyolefin is increasingly used for lightweight, heat-resistant components. Engine parts, interior fixtures, and structural elements benefit from the material’s combination of strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance. Using thermoplastic polyolefin for prototypes or molds helps streamline the transition from design to production.
Aerospace and Industrial Components
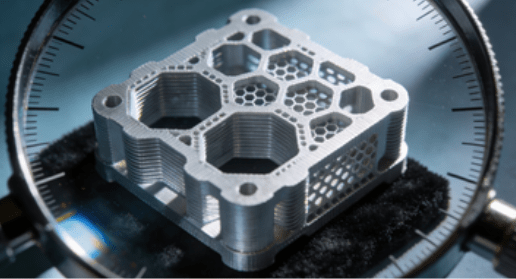
High-performance parts in aerospace and industrial applications require tight tolerances, chemical resilience, and mechanical reliability. Thermoplastic polyolefin is well-suited to these requirements, allowing manufacturers to produce precision components that meet rigorous standards for safety and durability.
Material Comparison Table
| Material | Strength | Thermal Resistance | Chemical Resistance | Cost Efficiency | Ease of Post-Processing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermoplastic Polyolefin | High | High | Excellent | Moderate | Easy |
| ABS | Moderate | Moderate | Fair | Low | Moderate |
| PLA | Low | Low | Poor | Low | Easy |
| Nylon | High | High | Good | Moderate | Moderate |
| Polycarbonate | High | High | Good | High | Difficult |
The table illustrates why thermoplastic polyolefin is often preferred for applications requiring a combination of strength, chemical resistance, and process adaptability.
Advantages of Using Thermoplastic Polyolefin in 3D Printing Casting

The advantages of thermoplastic polyolefin extend well beyond its fundamental material properties. For professionals in the 3D printing casting sector, these benefits translate into tangible improvements in production efficiency, product quality, and overall workflow reliability. By leveraging these advantages, manufacturers can reduce costs, increase yield, and produce components that meet strict performance standards.
Reduced Material Waste
One of the most immediate benefits of thermoplastic polyolefin is its low shrinkage rate during printing. This characteristic ensures that the final prints closely match the intended design, minimizing the need for rework or additional adjustments. In practical terms, this reduces material loss and increases the cost-efficiency of 3D printing casting operations. For industries where precision is critical, such as aerospace or automotive, this can significantly lower waste-related costs and improve sustainability.
Enhanced Accuracy and Precision
Dimensional stability is a critical factor in casting workflows, particularly for mold inserts and functional prototypes. Thermoplastic polyolefin maintains high dimensional accuracy even under varying thermal conditions. This ensures that parts consistently meet tight tolerances, reducing assembly issues and improving the reliability of casted components. Enhanced precision also supports rapid prototyping, allowing engineers to test complex designs without the risk of distortion.
Improved Durability
Thermoplastic polyolefin combines toughness with flexibility, making it less prone to cracking, warping, or other mechanical failures during post-processing. Components made from this material can endure sanding, coating, or other finishing processes without losing structural integrity. This durability is especially valuable for high-performance parts in automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications, where consistent quality and long-lasting performance are required.
Cost Savings in Production
Ease of printing and post-processing makes thermoplastic polyolefin a cost-effective choice for 3D printing casting operations. Reduced finishing requirements, fewer failed prints, and minimal rework translate to lower labor costs and faster production cycles. Over time, these efficiencies contribute to a significant reduction in overall production costs compared to traditional polymers like ABS or PLA.
Compatibility with Hybrid Manufacturing
Thermoplastic polyolefin is highly versatile and can be integrated with metals, ceramics, and other polymers to create composite structures. This compatibility enables engineers to design hybrid components that leverage the strengths of multiple materials. For example, a 3D-printed polyolefin pattern may serve as a temporary mold for metal casting, or be combined with reinforced polymers to create parts with enhanced mechanical properties. This versatility expands the range of possible applications and supports innovation in product design.
Considerations When Using Thermoplastic Polyolefin for Casting
While thermoplastic polyolefin offers a wide range of benefits, successful application requires careful attention to several key considerations. Proper planning and design can maximize performance and prevent potential issues in 3D printing casting workflows.
Printer Settings and Compatibility
Not all 3D printers are optimized for thermoplastic polyolefin. To achieve high-quality prints, it is essential to verify that the printer can handle the material’s thermal and mechanical requirements. Adjustments such as appropriate extrusion temperatures, print speeds, and layer heights are often necessary. Ensuring compatibility with your printer prevents failed prints and material waste, contributing to consistent results.
Post-Processing Techniques
Depending on the intended use, thermoplastic polyolefin parts may require post-processing to achieve the desired surface finish or functional characteristics. Techniques such as sanding, coating, or curing can enhance durability and improve aesthetic quality. Manufacturers should plan post-processing steps in advance to ensure that they complement the properties of the material without introducing new issues, such as warping or deformation.
Environmental Factors
The long-term performance of thermoplastic polyolefin can be affected by environmental conditions. Exposure to UV light, high humidity, or fluctuating temperatures may impact material stability over time. Proper storage, handling, and, if necessary, protective coatings can help maintain the quality of parts, especially for molds or patterns intended for repeated use.
Cost Analysis
Although thermoplastic polyolefin is moderately priced, production costs should account for more than just raw material expenses. Factors such as printer wear, labor for post-processing, and potential trial runs for complex geometries must be considered. Conducting a full cost analysis ensures that the use of thermoplastic polyolefin is financially viable and aligns with project budgets.
Design Adjustments
Complex geometries and intricate features may require additional design considerations. Support structures, wall thickness adjustments, and tolerances for shrinkage should be incorporated into the design phase to fully leverage the material’s strengths. Planning these adjustments early helps reduce trial-and-error iterations and improves overall production efficiency.
By addressing these considerations early in the design and production phases, manufacturers can maximize the performance benefits of thermoplastic polyolefin. A proactive approach ensures high-quality outputs, reduces potential errors, and supports efficient 3D printing casting operations across a variety of industrial applications.
Conclusion
Thermoplastic polyolefin represents a versatile, durable, and high-performance material for 3D printing casting applications. Its combination of chemical resistance, thermal stability, and process adaptability makes it a must-have for industries demanding precision and reliability. From prototyping to production molds, thermoplastic polyolefin ensures consistent results, reduced material waste, and enhanced product quality.
For engineers and designers seeking to optimize their casting workflows, understanding the unique benefits and limitations of thermoplastic polyolefin is crucial. When applied correctly, it can significantly elevate both the efficiency and the quality of 3D printed components, making it a cornerstone material in modern additive manufacturing processes.
FAQ
Q1: Can thermoplastic polyolefin be used in all 3D printing technologies?
A1: Thermoplastic polyolefin is compatible with FDM, SLS, and certain resin-based printing techniques, but printer settings must be adjusted for optimal performance.
Q2: How does thermoplastic polyolefin compare to ABS or PLA for casting?
A2: Compared to ABS or PLA, thermoplastic polyolefin offers higher chemical resistance, better thermal stability, and reduced shrinkage, making it ideal for functional prototypes and molds.
Q3: Is post-processing required for thermoplastic polyolefin prints?
A3: Depending on the application, post-processing such as sanding, coating, or curing may be needed to achieve smooth finishes or improve mechanical properties.
Q4: What industries benefit most from thermoplastic polyolefin casting?
A4: Automotive, aerospace, industrial components, and prototyping sectors benefit most due to the material’s strength, chemical resistance, and precision.
Q5: Are there environmental considerations when using thermoplastic polyolefin?
A5: Yes, it is sensitive to UV exposure, humidity, and extreme temperatures, so proper storage and handling are essential to maintain performance.
Product Categories
- Valve Parts
- Water Pump Parts
- Bearing Box Parts
- Die Casting Parts
- Stainless Steel Pump Products
- Cast Iron Pump Products
- Valve Parts For Automobile Use
- Auto Parts
- Valve Parts For Civil Use
- Vacuum Pump Parts KF

