6 Powerful Trends in 3D Printing Companies
Welcome to My Blog!
I’m thrilled to have you here! Before we dive into the content, I’d love for you to join me on my social media platforms. It’s where I share extra insights, connect with our amazing community, and keep you updated on the latest news. Here’s how you can stay connected:
📘 Facebook: Shanghai Leierwo Industry Trade Co., Ltd.
Now, let’s embark on this journey together! I hope you find the content here not only insightful but also inspiring and valuable. Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
Key Insights You’ll Gain From This Blog
- Emerging and disruptive technologies shaping 3D printing companies
- Material innovations and multi-material applications
- Industry-specific case studies: automotive, aerospace, medical, robotics
- Advantages of additive manufacturing versus traditional subtractive methods
- Global adoption trends and production scalability
- Expert opinions on the future of 3D printing companies
Additive manufacturing has fundamentally changed the way products are designed, prototyped, and produced. Today, 3D printing companies are no longer niche providers—they are global leaders in flexible, precise, and cost-effective production solutions. Leveraging technologies like MJF, SLA, SLS, and SLM, modern 3D printing companies can meet demands from single-piece customizations to large-scale industrial production, all while maintaining high precision.
The rapid adoption of 3D printing companies across industries is fueled by their ability to create complex geometries, reduce waste, and accelerate time-to-market. In fact, a 2025 industry report from Wohlers Associates notes that the global additive manufacturing market is projected to surpass $28 billion by 2026, with industrial 3D printing companies contributing the largest share.
Advanced Materials Driving Innovation in 3D Printing Companies
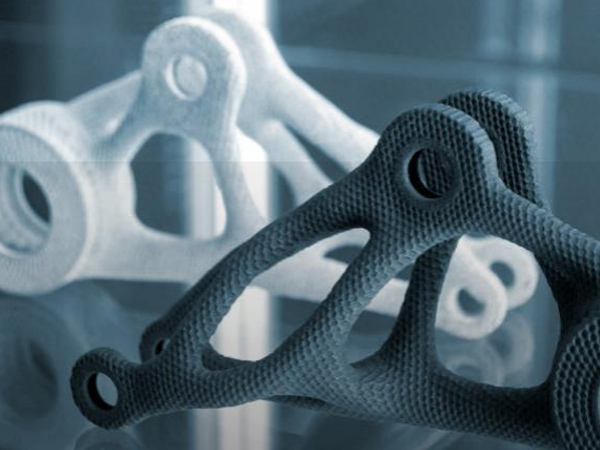
Multi-Material Flexibility
Leading 3D printing companies now offer a wide range of materials including metals (aluminum, titanium, stainless steel), plastics (PA12, ABS, high-performance nylon), and ceramics.
Multi-material printing allows for combining different physical properties in a single part—such as flexible joints with rigid structures—enabling designers to create products previously impossible with traditional manufacturing.
Material Advantages in Industry
- Aerospace: Titanium alloys reduce component weight while maintaining structural integrity.
- Medical: Biocompatible resins and metals allow patient-specific prosthetics.
- Automotive: Lightweight thermoplastics improve fuel efficiency without sacrificing durability.
3D printing companies strategically select materials to meet mechanical, thermal, and chemical requirements, ensuring high-quality output across sectors.
Cutting-Edge 3D Printing Technologies
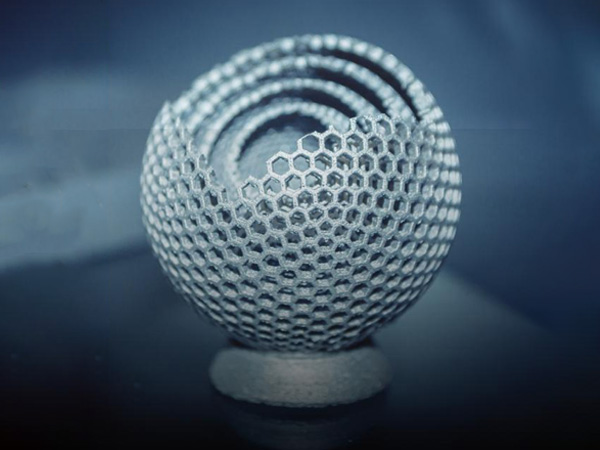
MJF Multi Jet Fusion

3D printing companies use MJF to produce high-precision parts rapidly.
- Material options: High-performance nylon, HP PA12
- Max build size: 332 x 189 x 274 mm
- Lead time: as short as 24 hours
SLM Selective Laser Melting

SLM allows 3D printing companies to fabricate complex metal parts for aerospace and medical applications.
- Max build size: 1258 x 1258 x 1600 mm
- Key benefit: Achieves tight tolerances and high structural integrity
SLA & SLS Printing
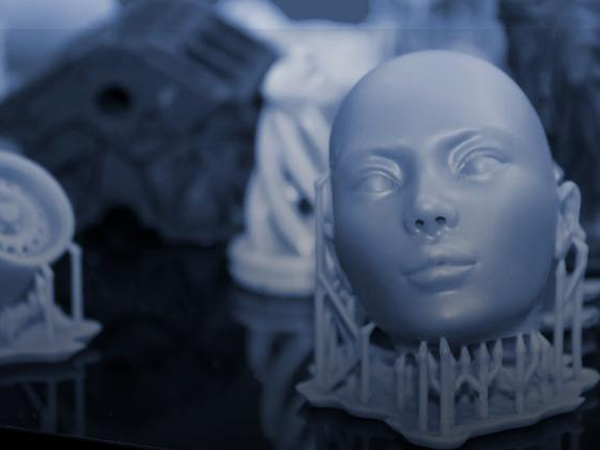
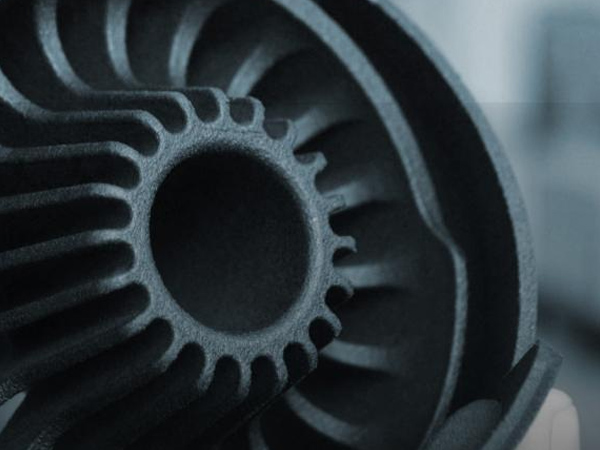


SLA produces highly detailed models, perfect for prototyping, while SLS offers durable, functional parts for industrial use.
- SLA build volume: 2100 x 1700 x 810 mm
- SLS build volume: 420 x 420 x 450 mm
Expert insight: According to Dr. Laura Michaels, a senior additive manufacturing researcher at MIT, “Integrating SLA and SLS allows 3D printing companies to balance surface finish quality and functional durability, making production both versatile and cost-effective.”
Industry Applications Driving Growth
Automotive Innovations

3D printing companies fabricate custom and replacement parts for vehicles, from engine components to tire molds.
- Enables rapid prototyping and small-batch production
- Reduces weight by up to 30% for certain parts
- Supports lightweight and personalized vehicle design
Aerospace Advancements

- Rocket engines, satellite propellant tanks, and airframe components
- Weight reduction up to 40% while maintaining performance
- Minimizes thermal stress during operation
Case study: Airbus has partnered with industrial 3D printing companies to manufacture over 1,000 flight-critical components per aircraft using SLM and titanium powders.
Medical Applications
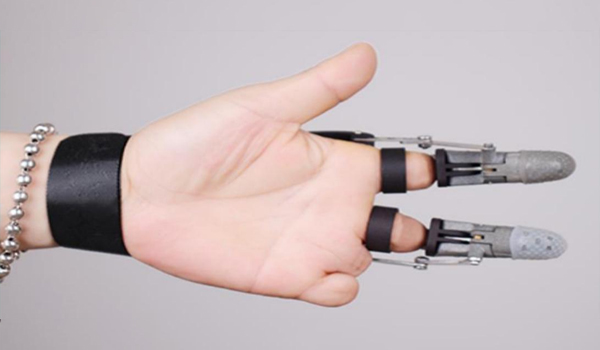
- Prosthetics, surgical guides, and assistive devices
- Customized designs improve patient comfort and reduce production time
- Cost reduction up to 50% compared to traditional methods
Robotics and Drones


- Rapid prototyping of housings, fan brackets, and precision mechanical parts
- Enables functional testing of near-final parts
- Supports high-volume and high-precision manufacturing
Art & Design

3D printing companies enable artists to produce sculptures with complex geometries that were impossible to create via subtractive methods.
- Fine surface finishes
- Complex internal structures
Benefits of Collaborating With a 3D Printing Company
Rapid Prototyping
From concept to prototype in hours to days, 3D printing companies accelerate design validation.
High Precision & Quality
- Tight tolerances achievable
- Surface treatments: electroplating, painting, annealing, grinding
- Reduces post-processing time
Flexible Production Volumes
- Single-unit production to 100,000+ pieces
- Cost-efficient for small-batch and large-scale production
Data-Driven Manufacturing
3D printing companies leverage AI and CNC-controlled systems to ensure consistency, minimize errors, and optimize throughput.
Comparison Table: Popular 3D Printing Technologies
| Technology | Material Types | Max Build Size (mm) | Lead Time | Key Industries |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MJF | Nylon, PA12 | 332 x 189 x 274 | 24h | Automotive, Prototyping |
| SLM | Metal powders | 1258 x 1258 x 1600 | 72h | Aerospace, Medical |
| SLA | Resins | 2100 x 1700 x 810 | 8h | Design, Prototyping |
| SLS | Nylon | 420 x 420 x 450 | 72h | Industrial parts, Robotics |
This table helps decision-makers evaluate the right technology when choosing a 3D printing company.
Emerging Trends in 3D Printing Companies

The landscape of additive manufacturing is evolving rapidly, and 3D printing companies are at the forefront of technological, operational, and industrial innovation. Staying updated on emerging trends is crucial for businesses looking to leverage these capabilities for competitive advantage. Here are six powerful trends shaping the industry in 2026 and beyond.
Trend 1: Automation & AI Integration
Automation and artificial intelligence are revolutionizing 3D printing companies, enabling higher efficiency and consistent quality across production lines. AI algorithms can predict potential defects, optimize material usage, and automatically adjust printing parameters in real time.
- Scheduling & Workflow Optimization: AI-driven software monitors machine status and production queues, dynamically prioritizing tasks to maximize throughput.
- Quality Control: Automated vision systems can detect layer defects and deviations from CAD models, reducing scrap rates by up to 15%, according to a 2025 report by Wohlers Associates.
- Material Optimization: AI models analyze material consumption patterns and recommend adjustments, minimizing waste and improving cost efficiency.
Example: A leading European 3D printing company reported a 20% increase in productivity after integrating AI-driven monitoring across 50 printers, demonstrating how technology enables scalable and repeatable production.
Trend 2: Sustainability Focus
Sustainability is becoming a core strategic priority for 3D printing companies as industries face stricter environmental regulations and consumer demand for greener production.
- Recyclable & Biodegradable Materials: High-performance polymers and biodegradable resins allow manufacturers to reuse materials, reducing landfill waste.
- Energy-Efficient Printers: Modern machines consume 30–40% less energy than older models, helping companies reduce operational costs and carbon footprint.
- Reduced Waste: Additive manufacturing inherently reduces material waste compared to subtractive methods, but combining process optimization with sustainable materials further improves efficiency.
Case Study: A North American 3D printing company implemented a closed-loop recycling system for PA12 nylon powder, achieving a 25% reduction in raw material consumption over one year.
Trend 3: Multi-Material Printing
The ability to print multiple materials in a single build is transforming the capabilities of 3D printing companies. By combining metals, plastics, and composites, manufacturers can produce multifunctional components that were previously impossible.
- Functional Integration: Parts can now combine rigid and flexible zones, high-strength cores with lightweight shells, or conductive and insulating segments.
- High-Performance Components: Aerospace and automotive industries benefit from parts that integrate heat-resistant metals with lightweight polymers, enhancing efficiency and durability.
Expert Insight: Dr. Michael Chen, a materials engineer at MIT, notes: “Multi-material printing is not just a technological advancement—it enables design freedom and performance optimization at a level traditional manufacturing cannot match.”
Trend 4: Speed & Lead Time Reduction
Time-to-market pressure is driving 3D printing companies to accelerate production cycles. Rapid prototyping is now complemented by high-speed production-grade printers capable of delivering industrial-quality parts within days.
- Faster Production Cycles: Layer-by-layer printing advancements and parallelization of multiple print heads reduce lead times by 30–50%.
- Reduced Prototyping-to-Production Timelines: Companies can move from design verification to functional end-use parts in as little as 48 hours, enabling agile responses to market demands.
Example: In the automotive sector, a European 3D printing company reduced the prototyping cycle for engine components from six weeks to just 72 hours using MJF and SLA hybrid setups.
Trend 5: Expanded Industrial Applications
The versatility of additive manufacturing allows 3D printing companies to enter diverse industries beyond traditional aerospace and automotive applications.
- Construction: Large-scale 3D printing creates architectural structures and concrete molds for modular buildings.
- Fashion & Consumer Goods: Designers can produce complex, customized items such as jewelry, footwear, and eyewear.
- Food Industry: Edible 3D printing is emerging for chocolates, pastries, and personalized nutrition products.
- Electronics: 3D printing enables prototypes for wearable devices, circuit boards, and complex housings.
This diversification helps 3D printing companies mitigate risks associated with dependence on a single industry while promoting innovation across sectors.
Trend 6: On-Demand & Decentralized Manufacturing
Global supply chains are under pressure due to shipping delays, tariffs, and localized demand. 3D printing companies are adopting decentralized, on-demand manufacturing models to respond efficiently.
- Local Production Hubs: Printing closer to the point of use reduces shipping costs, lead time, and carbon footprint.
- Responsive Networks: Companies are leveraging cloud-based production management systems to distribute orders across multiple locations, ensuring rapid fulfillment.
- Inventory Reduction: On-demand production minimizes the need for large inventories, reducing storage costs and mitigating risks of overproduction.
Industry Insight: According to McKinsey, decentralized additive manufacturing can cut logistics costs by up to 25% and reduce lead time by 40%, making it an attractive strategy for 3D printing companies aiming to compete globally.
Challenges Facing 3D Printing Companies
Cost of Advanced Equipment
High initial investment in industrial printers remains a barrier for small companies.
Skill & Expertise
Skilled engineers are required to optimize designs for additive manufacturing.
Material Limitations
Certain metals and resins are expensive or have limited availability, affecting scalability.
Comparison: While traditional CNC machining excels in large-volume, simple parts, 3D printing companies outperform in complex geometries, personalization, and waste reduction.
Conclusion
The growth of 3D printing companies reflects a broader shift toward additive manufacturing as a mainstream industrial technology. By embracing multi-material printing, AI-driven automation, sustainable practices, and rapid prototyping, these companies are redefining production efficiency, precision, and flexibility.
Businesses partnering with a leading 3D printing company can achieve:
- Reduced time-to-market by 25%
- Lower product development costs by 30%
- High-precision, complex parts with flexible volumes
- Sustainable and cost-effective production
The future of manufacturing is additive, and 3D printing companies are at the forefront, delivering innovation across industries worldwide.
FAQ
Q1: What materials can a 3D printing company work with?
A1: Metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites. Each material serves different industrial needs—from aerospace to medical devices—and supports high-precision manufacturing.
Q2: How do 3D printing companies ensure high precision?
A2: Technologies like SLM, SLA, and MJF, combined with CNC post-processing and digital inspection, guarantee tight tolerances and surface finish.
Q3: Are small-batch productions cost-effective?
A3: Yes. 3D printing companies eliminate tooling costs, making small batches economically viable.
Q4: How long does prototyping take?
A4: SLA parts can be delivered in 8 hours, MJF in 24 hours, and SLM metal parts in 72 hours.
Q5: Can 3D printing companies handle complex geometries?
A5: Absolutely. Layer-by-layer printing captures intricate designs impossible for traditional subtractive methods.
Q6: How are surface finishes handled?
A6: Treatments include electroplating, painting, annealing, grinding, dyeing, and silk-screening.
Q7: How is sustainability addressed?
A7: Many 3D printing companies use recycled materials, energy-efficient machines, and minimize scrap to reduce environmental impact.
Q8: Which industries benefit most from 3D printing companies?
A8: Aerospace, automotive, medical, robotics, consumer products, art & design, and small-batch manufacturing.
Q9: Can production be scaled from prototype to mass production?
A9: Yes. Modern 3D printing companies provide end-to-end solutions from prototype to 100,000+ units.
Q10: How does AI help 3D printing companies?
A10: AI optimizes production schedules, detects potential defects, and enhances material usage efficiency, reducing costs and lead times.
Product Categories
- Valve Parts
- Water Pump Parts
- Bearing Box Parts
- Die Casting Parts
- Stainless Steel Pump Products
- Cast Iron Pump Products
- Valve Parts For Automobile Use
- Auto Parts
- Valve Parts For Civil Use
- Vacuum Pump Parts KF

