Gray Iron Foundry Processes Explained
Table of Contents
Introduction to Gray Iron Foundries
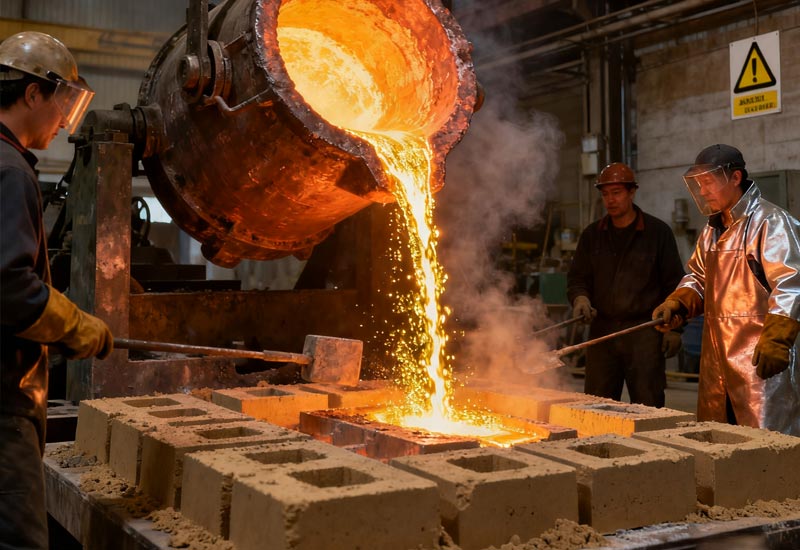

A gray iron foundry is a specialized facility dedicated to the production of gray cast iron components, widely used in industrial machinery, automotive systems, energy equipment, and infrastructure. Known for its superior vibration damping, machinability, and cost efficiency, gray iron remains one of the most extensively utilized materials in metal casting. This guide expands on the core concepts behind gray iron foundry operations, supplemented with comparisons, engineering insights, real-world case studies, and practical explanations that help engineers, buyers, and technical professionals evaluate casting options effectively.
Understanding Gray Cast Iron Basics in a Gray Iron Foundry
What Is Gray Cast Iron?
Gray cast iron is an iron-carbon alloy characterized by the presence of graphite flakes. These flakes create a gray-colored fracture surface and influence its mechanical properties, including damping capacity and machinability.
Concept: Graphite Flake Structure
Graphite flakes disperse through the iron matrix and act as natural chip breakers during machining. Their unique shape reduces vibration and enhances thermal conductivity, making the material ideal for components requiring stability and precision.
Key Properties of Gray Iron
- High vibration damping
- Good thermal conductivity
- Excellent machinability
- Strong compressive strength
Why Gray Cast Iron Remains Popular
Gray iron offers a balance of performance and affordability. It continues to dominate industries that require thermal stability, precise machining, and high compressive strength.
Gray Iron Foundry Production Processes
Pattern Making for Gray Iron Castings
Patterns serve as the dimensional blueprint for the final casting. They may be produced using wood, aluminum, resin, or even 3D printing for highly detailed shapes.
Concept: Dimensional Allowance
Patterns incorporate adjustments for shrinkage, machining stock, and mold draft angles. These allowances ensure that castings achieve accurate tolerances after production and finishing.
Molding Techniques Used in a Gray Iron Foundry

Green Sand Molding
This process uses clay-bonded sand to form molds. It is known for low cost, high production efficiency, and versatility across various casting sizes.
Resin Sand Molding
Resin-bonded sand produces stronger molds with improved dimensional accuracy. This method is ideal for complex shapes or castings requiring smoother surfaces.
Lost Foam Casting
The lost foam process uses foam patterns that evaporate during metal pouring. It eliminates the need for parting lines and allows for highly intricate geometries.
Melting Methods in Gray Iron Foundries
Gray iron is typically melted using cupola furnaces or induction furnaces.
Cupola Furnace
A cupola furnace uses coke and scrap iron, making it a cost-effective option for large-volume production.
Induction Furnace
Induction furnaces offer cleaner melting, precise temperature control, and improved metallurgical stability. They are widely used for high-quality or high-grade castings.
Pouring, Cooling, and Solidification
The molten iron is poured into the prepared molds and allowed to cool. Cooling rate, mold material, and casting geometry heavily influence the final microstructure.
Concept: Solidification Rate
Quick cooling produces finer graphite flakes for improved strength, while slower cooling encourages larger flakes for better damping. Foundries adjust mold materials and thickness to control these outcomes.
Cleaning and Surface Conditioning
After shakeout, castings undergo shot blasting, grinding, and visual inspection. Finishing ensures components meet structural integrity and surface criteria.
Concept: Dimensional Consistency
Stable mold designs and controlled solidification reduce warpage and distortion, particularly important for engine components and machine base plates.
Comparative Technical Table: Gray Iron vs Ductile Iron vs Cast Steel
| Parameter / Material | Gray Cast Iron (GCI) | Ductile Iron (DI) | Cast Steel (CS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graphite Structure | Flake graphite | Nodular graphite | None |
| Tensile Strength Range | 150–350 MPa | 400–900 MPa | 450–1,000+ MPa |
| Compressive Strength | Very high | High | High |
| Vibration Damping | Excellent | Good | Low |
| Machinability | Excellent | Good | Fair/Low |
| Thermal Conductivity | High | Medium | Medium |
| Cost Level | Low | Medium | High |
| Best Application Type | Stability + precision | Strength + impact | High stress load |
Concept: Why These Differences Matter
Understanding these values helps engineers select the optimal material for their design—especially when balancing cost, machinability, and performance under stress.
Common Gray Iron Casting Products

Automotive Components
Engine blocks, brake rotors, and cylinder liners benefit from gray iron’s thermal stability and vibration damping.
Machinery Bases and Frames
Machine tool beds and equipment housings rely on gray iron to minimize vibration and maintain accuracy.
Pump and Valve Housings
Its dimensional stability and corrosion resistance make gray iron suitable for pump bodies, compressor housings, and valve components.
Construction and Infrastructure Components
Pipe fittings, manhole covers, and counterweights often use gray iron for its strength and cost-effectiveness.
Gray Iron Grades and Standards
ASTM A48 Classes
- Class 20
- Class 30
- Class 40
Each class offers varying tensile strength levels, damping capacity, and ideal application scenarios.
EN-GJL Grades
- EN-GJL-150
- EN-GJL-200
- EN-GJL-250
- EN-GJL-300
Concept: Tensile Strength Variation
Higher-grade gray irons provide better tensile strength but reduced damping. Selecting the right grade requires evaluating mechanical demands and service conditions.
Comparison of Gray Iron with Other Engineering Materials
When selecting materials for industrial components, understanding the strengths and limitations of each option is crucial. A Gray Iron Foundry specializes in producing components with properties tailored to various industrial requirements. Comparing gray iron with other engineering materials such as ductile iron, cast steel, and aluminum helps engineers make informed decisions for performance, cost, and longevity.
Gray Iron vs Ductile Iron
Gray iron offers excellent vibration damping, noise reduction, and machinability, which are key for precision components and stability-critical machinery. In contrast, ductile iron provides higher tensile strength and superior impact resistance, making it ideal for load-bearing parts and structural applications.
In a Gray Iron Foundry, controlling graphite morphology and casting parameters ensures that gray iron components achieve consistent damping and compressive performance. Real-world applications show that gray iron is preferred for machine tool bases, engine blocks, and brake rotors, while ductile iron is often selected for shafts, gears, and heavy-load brackets.
Practical Insight
For engineers evaluating materials, gray iron is optimal when precision, vibration control, and machinability are priorities. Ductile iron, however, is better suited for parts that must endure high tensile stresses or shock loading.
Gray Iron vs Cast Steel
Cast steel exhibits higher ductility and toughness, which makes it capable of withstanding high impact and fatigue conditions. However, producing cast steel components in a Gray Iron Foundry context is generally more expensive and requires extensive machining, making it less economical for many standard applications.
Gray iron maintains advantages in compressive strength, thermal stability, and dimensional accuracy, particularly for parts such as pump housings, valve bodies, and industrial machinery frames. Foundries often leverage these properties to produce components that perform reliably under load while reducing production cost.
Engineering Perspective
The choice between gray iron and cast steel involves balancing cost, machinability, and mechanical performance. Gray iron is the preferred solution when thermal stability, damping, and economical manufacturing are more critical than extreme tensile performance.
Gray Iron vs Aluminum Castings
Aluminum castings provide the benefit of low weight, corrosion resistance, and ease of handling. Yet, gray iron produced in a Gray Iron Foundry surpasses aluminum in compressive strength, wear resistance, and thermal stability—qualities essential for high-load and high-temperature environments.
For example, heavy machinery housings, brake components, and industrial pump casings rely on gray iron for its ability to maintain dimensional stability under repeated thermal cycles. Additionally, gray iron’s graphite content facilitates machining, reducing tool wear and allowing for precision finishing—advantages that aluminum cannot fully match.
Real-World Application
Industrial engineers often select gray iron castings over aluminum for equipment subjected to continuous vibration, heat, or heavy mechanical loads. A Gray Iron Foundry can optimize graphite flake size and distribution to meet specific thermal and mechanical performance requirements, ensuring long-lasting and reliable components.
How to Choose a Reliable Gray Iron Foundry

Selecting a dependable Gray Iron Foundry is critical to ensure the production of high-quality castings that meet performance and reliability requirements. Multiple factors should be considered, including technical capabilities, quality certifications, engineering support, and cost-effectiveness.
Evaluate Technical and Production Capabilities
A top-tier Gray Iron Foundry will be equipped with advanced molding lines, high-precision induction furnaces, and automated inspection systems. These capabilities ensure that each casting meets stringent dimensional and metallurgical standards. Foundries with modern equipment can produce complex geometries, maintain consistent graphite flake distribution, and reduce the risk of defects such as porosity or shrinkage cavities. Evaluating a foundry’s production processes allows customers to gauge whether it can handle both high-volume and high-precision casting requirements.
Check Certifications and Quality Systems
Reputable Gray Iron Foundries often hold certifications such as ISO 9001, IATF 16949, or similar quality management standards. These certifications signal that the foundry has a structured quality control system, traceable production records, and standardized inspection processes. Beyond paperwork, certifications indicate a commitment to consistency, reliability, and adherence to international manufacturing practices. Working with a certified foundry reduces risk and ensures that the final products meet regulatory and customer expectations.
Consider Engineering Support
The presence of an experienced engineering team in a Gray Iron Foundry can significantly impact the final quality of castings. Engineers assist with design optimization, mold flow analysis, and defect prevention strategies. They provide guidance on material selection, casting geometry, and solidification control. A foundry with strong engineering capabilities can suggest improvements that minimize post-processing, reduce machining time, and enhance the overall performance of the component.
Analyze Cost Factors
Cost evaluation goes beyond the price per kilogram of cast iron. In a Gray Iron Foundry, several factors affect total project cost, including tooling complexity, part weight, selected material grade, surface finish, and the need for additional machining. Understanding how each factor influences cost enables buyers to make informed decisions without compromising quality. For example, selecting the right grade of gray iron can improve durability and reduce maintenance costs, making the investment more economical over the component’s lifecycle.
Applications of Gray Iron in Key Industries
Automotive Industry
Gray iron castings are widely used in the automotive sector, particularly for brake discs, engine components, and structural housings. In a Gray Iron Foundry, precise control of graphite distribution ensures thermal stability and vibration damping, which are critical for high-performance vehicle parts. Manufacturers rely on gray iron for its ability to withstand continuous thermal cycling while maintaining dimensional accuracy.
Agricultural Machinery
Agricultural equipment demands durable, vibration-resistant components. A Gray Iron Foundry can produce tractor parts, transmission housings, and other high-load components optimized for mechanical stress. Proper casting design and material control help prevent fatigue and extend service life, even under harsh operating conditions.
Industrial Equipment
Industrial machinery such as compressors, gear casings, machine frames, and pump systems benefit from gray iron’s combination of strength, thermal stability, and vibration damping. By leveraging the expertise of a Gray Iron Foundry, engineers can ensure that complex industrial components maintain structural integrity and operational precision throughout their service life.
HVAC and Infrastructure
Gray iron castings are used extensively in compressors, piping systems, and municipal hardware. A Gray Iron Foundry can produce components that resist thermal expansion, corrosion, and mechanical wear, which is essential for reliable infrastructure and energy systems. These castings ensure long-term performance in both commercial and municipal applications.
Conclusion
Gray iron foundries remain essential to modern manufacturing by delivering durable, stable, and cost-effective cast iron components. Understanding its material properties, casting processes, and comparison with alternative materials offers engineers and buyers the knowledge needed to choose the right solution. From automotive systems to industrial machinery, gray iron continues to be a dependable material supporting countless applications worldwide.
FAQ
What does a gray iron foundry actually do?
A gray iron foundry melts raw materials, produces molds, casts iron components, and performs finishing and quality testing to meet engineering requirements.
Is gray iron durable enough for heavy equipment?
Yes. Gray iron has high compressive strength and thermal stability, making it suitable for machinery bases, engine components, and pump housings.
How do I decide between gray iron and ductile iron?
Choose gray iron for applications needing vibration damping and machinability. Choose ductile iron for parts exposed to high tensile loads or impact forces.
Why is gray iron more affordable than many other metals?
Its lower melting temperature, simple molding process, and widespread availability reduce overall production costs.
Can gray iron withstand high temperatures?
Gray iron handles heat well and maintains dimensional stability, which is why it’s used for brake rotors, furnace components, and compressor parts.
What factors influence the price of a gray iron casting?
Casting size, mold type, machining requirements, material grade, and surface finish are among the top cost drivers.
Is gray iron environmentally friendly?
Yes. Gray iron production often relies heavily on recycled scrap metal, contributing to sustainability and resource efficiency.
Stay Connected with Us

Thank you for reading! We hope this blog provided you with valuable insights and inspiration on acoustic panel ceilings. If you enjoyed the content and want to stay updated with the latest trends, tips, and behind-the-scenes updates, we’d love to connect with you on social media.
📘 Follow us on Facebook: Shanghai Leierwo Industry Trade Co., Ltd.
Join our growing community where we share expert advice, product highlights, and interactive discussions with professionals and design enthusiasts from around the world.
Let’s keep the conversation going—see you there!
Product Categories
- Valve Parts
- Water Pump Parts
- Bearing Box Parts
- Die Casting Parts
- Stainless Steel Pump Products
- Cast Iron Pump Products
- Valve Parts For Automobile Use
- Auto Parts
- Valve Parts For Civil Use
- Vacuum Pump Parts KF

