5 Powerful Pump Impeller Types That Boost Flow
Welcome to My Blog!
I’m thrilled to have you here! Before we dive into the content, I’d love for you to join me on my social media platforms. It’s where I share extra insights, connect with our amazing community, and keep you updated on the latest news. Here’s how you can stay connected:
📘 Facebook: Shanghai Leierwo Industry Trade Co., Ltd.
Now, let’s embark on this journey together! I hope you find the content here not only insightful but also inspiring and valuable. Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Discover 5 top pump impeller types that directly influence flow performance
- Understand real-world efficiency data and operational benefits
- Learn how to match impeller type to your fluid and system
- Compare impeller types with a professional decision matrix
- Understand common failure signals and how to avoid them
- Get actionable maintenance and procurement strategies
- Includes FAQ and comparison tables for quick B2B decisions
A Strong Start: Why Pump Impeller Type Is a Business Decision, Not Just a Technical Choice
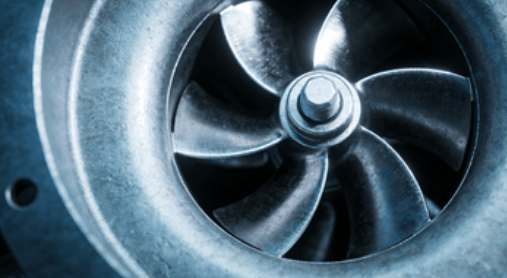
In industrial operations, pump performance is often measured by flow rate (Q), head (H), and efficiency (%). However, the hidden factor that most engineers and buyers underestimate is the pump impeller type. Choosing the wrong impeller type can cause up to 20–30% energy waste, increase downtime, and reduce pump life by 40% or more, according to Reliability Engineering studies published by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME).
A 2022 industry survey across manufacturing plants showed that impeller mismatches accounted for 15% of pump failures, and most were preventable through correct selection. In B2B procurement, this means that the impeller decision is not a “technical detail”—it is a risk management decision that affects CAPEX, OPEX, and operational stability.
Understanding Pump Impeller Types: The Basics
What Is an Impeller?
A pump impeller is the rotating part that transforms mechanical energy into hydraulic energy. It accelerates fluid outward using centrifugal force. Different pump impeller types change the fluid path, affecting performance.
Why Impeller Type Affects Flow
- Blade design affects velocity distribution
- Shroud design influences leakage and efficiency
- Clearance and geometry determine cavitation resistance
The Cost of Wrong Impeller Selection
Wrong impeller selection can lead to:
- Excessive vibration and noise
- Reduced efficiency
- Premature wear and corrosion
- Cavitation damage
- Higher energy bills
A widely cited study from the Hydraulic Institute notes that improper impeller selection is one of the top three causes of pump inefficiency in industrial systems.
The 5 Powerful Pump Impeller Types That Boost Flow
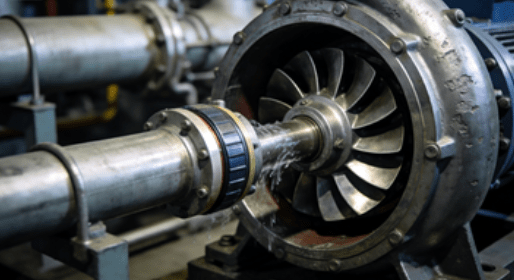
When selecting pump components, the choice of pump impeller types is not just a technical detail—it directly determines flow performance, energy efficiency, and maintenance cost. For industrial buyers, knowing which impeller type fits your fluid and operating conditions can prevent frequent downtime and reduce lifecycle cost. Below are the five most powerful pump impeller types that boost flow and improve system reliability.
Open Impeller (High Flow, Easy Maintenance)
What It Is
An open impeller is one of the most basic yet practical pump impeller types. The blades are attached only to a central hub without a full cover plate. This open structure allows more fluid to pass through with less restriction, making it ideal for fluids with particles or debris.
Why It Boosts Flow
Open impellers deliver high flow because the fluid can enter and exit the impeller with minimal blockage. The reduced internal pressure drop also improves volumetric efficiency, especially at low to medium head conditions.
Best Use Cases
- Wastewater and sewage systems
- Slurry pumping
- Low-viscosity fluids containing debris
- Agricultural irrigation with particulate matter
Efficiency and Performance Data
- Typical efficiency range: 40–60%
- Best for high flow, low-pressure systems
- Ideal when clogging is the primary concern
Common Advantages
- Excellent for solids handling
- Lower risk of clogging
- Simple structure reduces repair time
B2B Procurement Advantage
From a procurement perspective, open impeller pump impeller types offer lower maintenance costs due to easy access and cleaning. In heavy-duty environments, this can reduce labor hours and spare part costs significantly.
Semi-Open Impeller (Balanced Flow and Efficiency)
What It Is
Semi-open impellers are another common pump impeller types. They feature blades attached to a shroud on one side, offering a balance between open and closed designs. This structure reduces turbulence while still allowing solids to pass.
Why It Boosts Flow
Semi-open impellers provide a more stable flow path than open impellers. The partial shroud improves hydraulic efficiency and reduces internal recirculation, resulting in smoother flow and less vibration.
Best Use Cases
- Cooling systems
- General industrial pumping
- Chemical plants with low-to-medium solids
- Food processing with moderate particulate content
Efficiency and Performance Data
- Typical efficiency range: 55–70%
- Better than open impellers in energy consumption
- Still robust for solids handling
Key Advantages
- Balanced efficiency and maintenance
- Less sensitive to debris than closed impellers
- Lower vibration and noise
Procurement Insight
For B2B buyers, semi-open impeller pump impeller types are often the best “all-rounder” choice. They fit applications that need moderate efficiency without sacrificing reliability.
Closed Impeller (High Efficiency, Strong Flow Control)
What It Is
Closed impellers are considered the most efficient pump impeller types in many applications. Blades are enclosed between two shrouds, creating a controlled fluid path that reduces leakage and improves performance.
Why It Boosts Flow
Closed impellers offer stable flow and high hydraulic efficiency. The enclosed design minimizes internal recirculation, ensuring more energy is transferred to the fluid and less is lost to turbulence.
Best Use Cases
- Boiler feed systems
- HVAC systems
- High-pressure water systems
- Clean water pumping in industrial processes
Efficiency and Performance Data
- Typical efficiency range: 70–85%
- Suitable for clean fluids
- Provides strong head and stable flow
Limitations
Closed impellers are sensitive to debris and require clean fluid environments. If used in dirty fluids, the risk of clogging and wear increases dramatically.
Industry Expert Insight
The European Pump Manufacturers Association (Europump) highlights closed impellers as the benchmark for high-efficiency pumping in clean water applications. When energy savings and long-term reliability are priorities, closed impellers are often the top choice among pump impeller types.
Procurement Tip
When selecting closed impeller pump impeller types, buyers should prioritize:
- Fluid cleanliness
- Precise alignment
- Regular maintenance intervals
Vortex Impeller (Low Clogging, High Reliability)
What It Is
Vortex impellers are unique among pump impeller types. They create a vortex flow that moves fluid without direct contact between the fluid solids and the impeller blades. This design is excellent for handling solids without clogging.
Why It Boosts Flow
Vortex impellers maintain flow stability even in highly contaminated fluids. By keeping solids away from the blades, they reduce wear and prolong pump life, ensuring consistent flow.
Best Use Cases
- Sewage and wastewater
- Stormwater
- Industrial wastewater
- Food processing wastewater
Efficiency and Performance Data
- Typical efficiency range: 50–65%
- Excellent for high solids
- Lower head compared to closed impellers
Key Advantages
- Minimal clogging
- Lower maintenance
- Long service life in harsh environments
B2B Advantage
For industrial buyers, vortex impeller pump impeller types reduce downtime and maintenance costs. This is particularly valuable in systems where pump failure causes major production losses.
Split-Case Impeller (Large Flow, High Stability)
What It Is
Split-case impellers are used in split-case pumps designed for high flow and easy maintenance access. The impeller sits in a split casing, allowing technicians to access internal parts without disturbing piping.
Why It Boosts Flow
The large impeller size and optimized fluid path allow very high flow rates with stable performance. Split-case impellers are built for continuous operation and long-term reliability.
Best Use Cases
- Municipal water systems
- Water treatment plants
- Industrial cooling and process water
- Fire protection systems
Efficiency and Performance Data
- Typical efficiency range: 70–90%
- Ideal for continuous operation
- High reliability and long service life
Procurement Advantage
Split-case pump impeller types are favored in B2B procurement due to:
- Easy maintenance access
- Reduced downtime
- Stable performance in large systems
Key Notes for Buyers
When selecting split-case impeller pump impeller types, consider:
- System flow demand
- Pump footprint
- Installation complexityring labor costs and downtime.
Concept Section: How Impeller Design Affects Flow
Blade Angle and Flow Rate
Blade angle influences how the fluid is accelerated. A steeper blade angle increases flow rate but may increase energy consumption.
Cavitation Risk and Flow Stability
Cavitation occurs when pressure drops below vapor pressure, causing bubble formation. Proper impeller design reduces cavitation risk and protects pump lifespan.
Impeller Diameter and Pump Curve
Impeller diameter directly affects head and flow. A larger diameter increases head but may cause higher power consumption.
Common Pump Impeller Types: Decision Matrix for B2B Buyers
How to Choose Based on Fluid Type
- Solids-heavy fluids → Open or vortex impeller
- Clean water → Closed impeller
- Mixed debris → Semi-open impeller
How to Choose Based on System Requirements
- High flow needs → Split-case or open impeller
- High efficiency needs → Closed impeller
- Low maintenance needs → Vortex impeller
Pump Impeller Types Comparison Table (Quick Reference)
| Impeller Type | Flow Advantage | Efficiency | Best Use Case | Weakness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Open | High | 40–60% | Wastewater | Lower efficiency |
| Semi-Open | Balanced | 55–70% | Industrial | Moderate wear |
| Closed | Stable | 70–85% | High-pressure | Debris sensitive |
| Vortex | Anti-clog | 50–65% | Sewage | Lower head |
| Split-Case | Large volume | 70–90% | Municipal | Larger footprint |
Advanced Section: Real-World Data and Engineering Standards

Efficiency Impact on Energy Costs
In industrial pumping, energy accounts for up to 70% of total lifecycle costs. Selecting the correct impeller type can reduce energy consumption by 10–25% in many systems, according to the U.S. Department of Energy.
Industry Standards and Guidelines
Pump impeller design must comply with standards like:
- ISO 5199 (Technical specifications for centrifugal pumps)
- ISO 9906 (Hydraulic performance acceptance tests)
- ANSI/HI standards for pump design
What Engineers Look for in Impeller Design
Engineers evaluate:
- Hydraulic efficiency
- Vibration and noise
- Wear resistance
- Material compatibility
- Corrosion resistance
Maintenance Best Practices for Pump Impeller Types
Routine Inspection Checklist
- Inspect impeller for erosion and corrosion
- Check for vibration and abnormal noise
- Verify seal integrity
- Monitor flow and head changes
Preventing Cavitation
- Ensure correct NPSH (Net Positive Suction Head)
- Reduce suction lift
- Adjust impeller diameter or speed
Improving Service Life
Using correct impeller material can increase service life by 20–40%, especially in corrosive or abrasive fluids.
Final Thoughts: Selecting the Right Pump Impeller Type Is a Strategic Choice
Choosing the right pump impeller types is not just a technical decision—it affects your system performance, maintenance cost, and long-term reliability. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each impeller type, you can make a smarter procurement decision that boosts flow, reduces downtime, and improves overall efficiency.
FAQ
What is the best pump impeller type for high flow?
For high flow, split-case impellers and open impellers are often the best choices.
Can pump impeller types affect energy cost?
Yes, the impeller type impacts efficiency, and efficiency directly affects energy consumption. Closed impellers usually offer the best efficiency.
Which impeller type is best for dirty water?
Open or vortex impellers are best for dirty water because they resist clogging.
How often should impellers be inspected?
Impellers should be inspected every 3–6 months in industrial applications, depending on fluid quality and operating hours.
What causes impeller wear?
Impeller wear is often caused by abrasive solids, corrosion, cavitation, or poor lubrication.
Product Categories
- Valve Parts
- Water Pump Parts
- Bearing Box Parts
- Die Casting Parts
- Stainless Steel Pump Products
- Cast Iron Pump Products
- Valve Parts For Automobile Use
- Auto Parts
- Valve Parts For Civil Use
- Vacuum Pump Parts KF

