5 Key Factors Impacting Duplex Stainless Steel Investment Casting Quality
Welcome to My Blog!
I’m thrilled to have you here! Before we dive into the content, I’d love for you to join me on my social media platforms. It’s where I share extra insights, connect with our amazing community, and keep you updated on the latest news. Here’s how you can stay connected:
📘 Facebook: Shanghai Leierwo Industry Trade Co., Ltd.
Now, let’s embark on this journey together! I hope you find the content here not only insightful but also inspiring and valuable. Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
Introduction

In modern industrial applications, from chemical processing to offshore oil and gas platforms, the demand for components that combine exceptional corrosion resistance, high strength, and durability has never been higher. Duplex stainless steel investment casting meets this demand by providing a unique combination of mechanical and chemical properties that outperform traditional austenitic or ferritic stainless steels.
Recent studies by the International Stainless Steel Forum (ISSF) indicate that duplex stainless steel components reduce maintenance costs by up to 30% in harsh environments, thanks to their enhanced resistance to chloride-induced stress corrosion cracking. Moreover, the alloy’s high yield strength, often twice that of standard 304 stainless steel, allows engineers to design lighter components without compromising performance.
Despite these advantages, producing high-quality castings is highly sensitive to process parameters, material selection, and design choices. A small deviation can lead to porosity, microstructural imbalance, or premature failure. This article explores five key factors impacting duplex stainless steel investment casting quality, provides practical insights, includes real industrial data, and outlines standards to follow.
Material Selection: The Foundation of High-Quality Castings
Chemical Composition and Alloy Grade
Duplex stainless steel combines austenitic and ferritic phases, typically in a 50/50 balance, which provides both toughness and corrosion resistance. Selecting the correct grade is crucial. Common grades include:
- SAF 2205: Chromium 22%, Nickel 5–6.5%, Molybdenum 3%, ideal for chemical and marine applications.
- SAF 2507: Chromium 25%, Nickel 7%, Molybdenum 4%, used in aggressive chloride environments.
According to a 2021 study by the Nickel Institute, components cast with SAF 2507 exhibited a 45% improvement in pitting resistance compared to SAF 2205 under identical conditions.
Supplier Quality and Traceability
High-quality input materials reduce defects caused by inclusions or contamination. Engineers should always request certified mill test reports and verify chemical composition. Traceability is particularly important in industries like oil & gas, where failure could lead to safety hazards and costly downtime.
Microstructural Considerations
The ferrite-austenite balance directly affects corrosion resistance and toughness. ASTM A923 defines critical microstructural testing methods, including the Strauss test, to detect harmful intermetallic phases such as sigma phase.
Casting Process Control: Temperature, Mold, and Pouring Techniques

Mold Design and Thermal Management
Ceramic molds are standard in duplex stainless steel investment casting. Uniform wall thickness in molds ensures even heat distribution. Uneven cooling can produce residual stresses, increasing porosity and causing microstructural inconsistencies.
- Optimal mold thickness: 10–25 mm for medium-sized industrial components
- Thermal expansion consideration: Allow 1–1.5% expansion to avoid mold cracking
Pouring Temperature and Rate
Proper pouring temperature ensures complete filling while maintaining microstructural integrity:
- Recommended temperature range: 1450–1520°C
- Pouring too hot → Oxidation, coarse grains
- Pouring too cold → Misruns, cold shuts
A report from the ASM International highlights that variations of ±20°C can alter ferrite content by 5–10%, significantly affecting toughness.
Solidification and Cooling Rates
- Rapid cooling → Increased ferrite content, reducing ductility
- Slow cooling → Formation of intermetallic compounds, lowering corrosion resistance
- Industrial best practice → Controlled cooling rate of 15–25°C per minute for medium-thick sections
Design Considerations: Geometry, Wall Thickness, and Flow
Wall Thickness Uniformity
Non-uniform wall thickness leads to differential cooling, resulting in shrinkage defects and warping. For duplex stainless steel:
- Recommended maximum variation: ±20% for structural integrity
- Thicker sections may require risers to prevent shrinkage cavities
Radii and Fillets
Sharp corners concentrate stress and increase the risk of cracks. Recommended fillet radii:
- Small components: 2–4 mm
- Large components: 5–10 mm
Gating, Runners, and Pouring Channels
Proper design of gating systems reduces turbulence, minimizes oxide inclusions, and ensures uniform flow. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations are increasingly used to optimize metal flow in complex geometries.
Heat Treatment and Post-Casting Processing
Solution Annealing for Duplex Balance
Solution annealing ensures ferrite-austenite equilibrium and relieves internal stress:
- Temperature: 1020–1100°C
- Duration: 30–60 minutes (depending on section thickness)
- Rapid water quenching recommended
Post-annealing ensures high toughness, corrosion resistance, and dimensional stability.
Stress Relief and Machining Considerations
- Pre-machining stress relief minimizes distortion during cutting
- Recommended cutting speeds: 30–60 m/min for SAF 2205
- Lubricants containing sulfur or chlorine must be avoided to prevent corrosion initiation
Surface Quality and Inspection
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
- X-ray radiography: Detect internal voids or inclusions
- Ultrasonic testing: Measure thickness and internal defects
- Dye penetrant or magnetic particle testing: Surface crack detection
Surface Finish and Passivation
- Ra ≤ 0.8 µm recommended for aggressive environments
- Passivation enhances long-term corrosion resistance
Table: Typical Duplex Stainless Steel Investment Casting Specifications
| Application | Alloy Grade | Wall Thickness (mm) | Pouring Temp (°C) | Annealing Temp (°C) | Max Size (mm) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical valve body | SAF 2205 | 5–25 | 1480 | 1040 | 600 | High corrosion resistance |
| Pump impeller | SAF 2507 | 3–20 | 1500 | 1050 | 400 | Balanced microstructure |
| Marine propeller | SAF 2205 | 4–18 | 1475 | 1035 | 500 | Smooth surface finish |
| Oil & gas connector | SAF 2507 | 6–30 | 1510 | 1060 | 450 | High mechanical strength |
| Industrial valve housing | SAF 2205 | 5–25 | 1490 | 1045 | 700 | Uniform wall thickness |
Advanced Considerations: Industrial Standards and Expert Opinions
- ASTM A923: Microstructural evaluation methods
- ASTM A351/A743: Casting grade specifications
- Dr. Richard Davis, a metallurgist at ISSF, states:
“Maintaining precise phase balance and controlling cooling rates are the most critical factors in duplex stainless steel investment casting quality.” - European foundries increasingly adopt computer-aided mold design and real-time temperature monitoring, which reduces defects by up to 40%.
Common Defects and How to Prevent Them
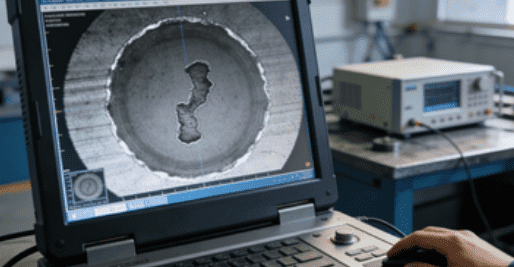
- Porosity → Controlled pouring temperature and degassing
- Cracks → Proper fillet radii, solution annealing
- Segregation → Uniform wall thickness, optimized gating
- Intermetallic formation → Controlled cooling, correct heat treatment
Conclusion
High-quality duplex stainless steel investment casting requires:
- Selecting proper alloy grades and certified suppliers
- Maintaining precise pouring temperature and mold design
- Designing uniform wall thickness and fillets
- Performing solution annealing and stress relief
- Conducting thorough NDT inspection and surface finishing
By addressing these five factors, manufacturers and buyers can ensure durable, corrosion-resistant, and precise components while reducing maintenance costs and extending service life.
FAQ
What are the most critical duplex stainless steel grades for casting?
SAF 2205 and SAF 2507 are commonly used due to their balance of corrosion resistance and mechanical strength.
Why is phase balance important?
Incorrect ferrite/austenite ratio can reduce toughness and corrosion resistance.
How do wall thickness variations affect quality?
Non-uniform walls can cause shrinkage, porosity, or warping.
What are the typical defects in duplex stainless steel casting?
Porosity, cracks, segregation, and intermetallic phases.
What heat treatment is recommended?
Solution annealing at 1020–1100°C with water quenching is standard.
Can CFD simulations help in casting design?
Yes, they optimize metal flow and reduce turbulence-induced defects.
How often should NDT inspections be performed?
Every critical component should undergo at least one full inspection before machining and surface finishing.
Product Categories
- Valve Parts
- Water Pump Parts
- Bearing Box Parts
- Die Casting Parts
- Stainless Steel Pump Products
- Cast Iron Pump Products
- Valve Parts For Automobile Use
- Auto Parts
- Valve Parts For Civil Use
- Vacuum Pump Parts KF

